Track AI-driven pull requests
As engineering teams integrate AI coding agents like GitHub Copilot, Claude, and Devin into their workflows, they face the challenge of managing an increased volume of pull requests. Tracking and reviewing these AI-generated contributions can be overwhelming without a centralized system. Port's AI control center addresses this issue by identifying pull requests originating from coding agents and displaying them in real-time, allowing you to efficiently monitor and act upon them.
Common use cases
- Act fast on AI agent contributions: Quickly respond to pull requests from AI coding agents using your AI control center.
- Quality assurance: Ensure AI-generated code meets your team's standards and review processes.
Prerequisites
This guide assumes the following:
- You have a Port account and have completed the onboarding process.
- Port's GitHub integration is installed in your account.
This guide assumes you're using GitHub to manage your code. However, the principles and steps outlined here can be adapted to other Git platforms such as GitLab, BitBucket etc.
Identifying AI-driven pull requests
Before tracking statuses, we need to identify whether a PR was created or influenced by an AI coding agent.
This logic differs depending on the agent:
- GitHub Copilot
- Claude Code
- Devin
How we detect it
- Copilot PRs are usually authored by the GitHub Copilot bot (
github-copilot[bot]). - They often start as draft PRs or use
"WIP"in the title. - Commits are signed with the Copilot signature.
Example
- PR title:
"WIP: Initial refactor". - Author:
github-copilot[bot]. - Draft:
true.
How we detect it
- PRs can be authored by either the human user or Claude itself. When authored by a human, Claude’s comments reveal its involvement.
- Claude typically adds long, structured review comments, often in a blockquote style or with headers like “Here’s what I changed”.
- No
draftor"WIP"markers are added automatically when authored by Claude.
Example
- Author:
janedoe(human) orclaude-bot. - Comment by Claude Code:
“Here are the changes I made for better error handling…”.
How we detect it
- Devin usually opens a regular PR (not draft, no WIP).
- Commits are authored by a dedicated GitHub user configured for Devin.
- Commit messages often follow a concise, imperative style (e.g.,
Fix API error handling).
Example
- PR: opened by
devin-bot(or the GitHub user assigned to Devin). - Commits:
author: Devin <bot@devin.ai>. - No draft/WIP markers.
Data model setup
We will create and configure blueprints to support tracking AI-driven pull requests. This includes setting up the AI coding agent blueprint and enhancing the existing pull request blueprint.
Creating AI coding agent blueprint
This blueprint will represent all known coding agents in your system.
-
Go to the Builder page of your portal.
-
Click on
+ Blueprint. -
Click on the
{...}button in the top right corner, and chooseEdit JSON. -
Copy and paste the following JSON schema:
AI Coding Agent blueprint (Click to expand)
{
"identifier": "ai_coding_agent",
"description": "This blueprint represents an AI coding agent",
"title": "AI Coding Agent",
"icon": "AI",
"schema": {
"properties": {},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"aggregationProperties": {
"total_p_rs_handled": {
"title": "Total PRs handled",
"type": "number",
"target": "githubPullRequest",
"calculationSpec": {
"func": "count",
"calculationBy": "entities"
}
},
"total_open_p_rs": {
"title": "Total open PRs",
"icon": "DefaultProperty",
"type": "number",
"target": "githubPullRequest",
"query": {
"combinator": "and",
"rules": [
{
"property": "status",
"operator": "=",
"value": "open"
}
]
},
"calculationSpec": {
"func": "count",
"calculationBy": "entities"
}
}
},
"relations": {}
} -
Click
Createto save the blueprint.
Ensure that this blueprint is populated with the names of coding agents such as Copilot, Claude, Devin, etc. This will help in accurately tracking and managing AI-driven pull requests.
Go to the catalog page for the AI Coding Agent blueprint and click on the + AI Coding Agent button to add these entities using the JSON provided below: Copilot entity JSON
{
"identifier": "Copilot",
"title": "Copilot",
"icon": "AI",
"properties": {},
"relations": {}
} Claude entity JSON
{
"identifier": "Claude",
"title": "Claude",
"icon": "AI",
"properties": {},
"relations": {}
} Devin entity JSON
{
"identifier": "Devin",
"title": "Devin",
"icon": "AI",
"properties": {},
"relations": {}
}
Update pull request blueprint
When installing Port's GitHub app, the Service and Pull request blueprints are created by default. However, we need to update the Pull request blueprint with new properties and add relations.
-
Go to the Builder page of your portal.
-
Find and select your existing
Pull requestblueprint. -
Click on
{...} Edit JSON. -
Add the following property to the
propertiessection:Draft and coding agent status property (Click to expand)
"draft": {
"icon": "DefaultProperty",
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Draft",
"description": "Whether the PR is in draft mode. Draft PR usually requires more attention."
},
"workStatus": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Coding agent status",
"description": "The most important status definition for a PR. \"Approved\" means needs to nudge reviewers/address comments, when \"Awaiting review\" requires urgent attention.",
"enum": [
"In Progress",
"Awaiting review",
"Requested changes",
"Approved",
"Unknown"
],
"enumColors": {
"In Progress": "yellow",
"Awaiting review": "orange",
"Requested changes": "turquoise",
"Approved": "green",
"Unknown": "lightGray"
}
} -
Add the following relation to the
relationssection:AI coding agent relation (Click to expand)
"ai_coding_agent": {
"title": "AI Coding Agent",
"target": "ai_coding_agent",
"required": false,
"many": true
} -
Click
Saveto update the blueprint.
Update GitHub integration configuration
Now we will update the GitHub integration configuration to ensure that the new properties added to the pull requests are correctly mapped.
-
Go to the data sources page of your portal.
-
Find your GitHub integration and click on it.
-
Go to the
Mappingtab. -
Add the following YAML block into the editor to map the pull request properties:
Updated GitHub integration configuration (Click to expand)
- kind: pull-request
selector:
query: "true"
port:
entity:
mappings:
identifier: .id|tostring
title: .title
blueprint: '"githubPullRequest"'
properties:
status: .status
closedAt: .closed_at
updatedAt: .updated_at
mergedAt: .merged_at
createdAt: .created_at
prNumber: .number
link: .html_url
labels: '[.labels[].name]'
branch: .head.ref
draft: .draft
workStatus: >-
if (.title | test("WIP"; "i")) then
"In Progress"
elif (.draft == true and ((.requested_reviewers // []) | length) >
0) then
"Awaiting review"
elif (.draft == true and (.title | test("WIP"; "i") | not) and
((.requested_reviewers // []) | length) == 0) then
"Requested changes"
elif (.draft != true) then
"Approved"
else
"Unknown"
end
leadTimeHours: >-
(.created_at as $createdAt | .merged_at as $mergedAt | ($createdAt
| sub("\\..*Z$"; "Z") | strptime("%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ") | mktime)
as $createdTimestamp | ($mergedAt | if . == null then null else
sub("\\..*Z$"; "Z") | strptime("%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ") | mktime end)
as $mergedTimestamp | if $mergedTimestamp == null then null else
(((($mergedTimestamp - $createdTimestamp) / 3600) * 100 | floor) /
100) end)
relations:
repository: .head.repo.nameWork Status JQ explanationThis JQ determines the work status of a PR based on:
- In Progress: PR title contains "WIP" (work in progress)
- Awaiting review: Draft PR with assigned reviewers
- Requested changes: Draft PR without reviewers (likely needs changes)
- Approved: Non-draft PR (ready for final review)
- Unknown: Any other state
The default workStatus mapping is optimized for GitHub Copilot, which usually opens draft PRs or adds "WIP" to titles.
For Claude or Devin, PRs are typically created as regular, non-draft PRs with no WIP indicators.
In that case, you can use this simplified mapping that relies only on reviewers and merge status:Alternative mapping for Claude/Devin PRs (Click to expand)
workStatus: >-
if ((.requested_reviewers // []) | length) > 0 then
"Awaiting review"
elif ((.requested_reviewers // []) | length) == 0 then
"In Progress"
else
"Unknown"
end
Set up automations
To effectively track the status of coding agents, we will create several automations. You have the flexibility to determine if a coding agent participated in a PR creation by examining its comments, commits, or both, depending on your specific needs. This allows you to tailor the tracking process to best fit your requirements.
Add Port secrets
Before setting up the automations, ensure you have added the necessary secrets to securely interact with the GitHub REST API within your portal. This is essential for accessing the required data.
To add the secret to your portal:
-
Click on the
...button in the top right corner of your Port application. -
Click on Credentials.
-
Click on the
Secretstab. -
Click on
+ Secretand add the following secret:GITHUB_TOKEN- Your GitHub fine-grained access token with access to read repository commits and comments.
Once the secret is added, you can proceed with setting up the automations based on your chosen method of tracking AI participation:
- Commits (AI wrote code)
- Comments (AI reviewed code)
Commits Automation Flow
This flow identifies AI involvement in code writing by analyzing commit data.
- Run automation to fetch commits for each PR update.
- Run second automation to extract and identify coding agent names from commits.
Automation 1: Get commits on PR updated
This automation only runs when the ai_coding_agent relation is null (before and after) to ensure that it only processes pull requests that have not yet been associated with an AI coding agent.
-
Go to the Automations page of your portal.
-
Click on
+ Automation. -
Copy and paste the following JSON schema:
Get commits on PR updated automation (Click to expand)
{
"identifier": "get_commits_on_pr_updated",
"title": "Get Commits on PR Updated",
"description": "Automation to get the commits upon PR updates",
"icon": "GitPullRequest",
"trigger": {
"type": "automation",
"event": {
"type": "ENTITY_UPDATED",
"blueprintIdentifier": "githubPullRequest"
},
"condition": {
"type": "JQ",
"expressions": [
".diff.before.relations.ai_coding_agent == []",
".diff.after.relations.ai_coding_agent == []"
],
"combinator": "and"
}
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "WEBHOOK",
"url": "{{ .event.diff.after.properties.link | sub(\"https://github.com/\"; \"https://api.github.com/repos/\") | sub(\"/pull/\"; \"/pulls/\") + \"/commits\" }}",
"agent": false,
"synchronized": true,
"method": "GET",
"headers": {
"Accept": "application/vnd.github+json",
"Authorization": "Bearer {{ .secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}",
"X-GitHub-Api-Version": "2022-11-28",
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Identifier": "{{ .event.context.entityIdentifier | tostring }}",
"Pr-Link": "{{ .event.diff.after.properties.link }}"
},
"body": {}
},
"publish": true
} -
Click
Createto save the automation.
Automation 2: Update PR with AI coding agent (commit-based)
This automation only runs if the commits response contains a match for AI agents, ensuring that only relevant pull requests are updated with AI coding agent information.
-
Go back to the Automations page of your portal.
-
Click on
+ Automation. -
Copy and paste the following JSON schema:
Update PR with AI coding agent using commit automation (Click to expand)
{
"identifier": "update_pr_with_ai_coding_agent",
"title": "Update PR with AI Coding Agent Using Commit",
"description": "Automation to update the PR with the AI coding agent involved in it (from commits)",
"icon": "GitPullRequest",
"trigger": {
"type": "automation",
"event": {
"type": "RUN_UPDATED",
"actionIdentifier": "get_commits_on_pr_updated"
},
"condition": {
"type": "JQ",
"expressions": [
".diff.after.status == \"SUCCESS\"",
".diff.before.response | [ .[] | (.commit.author.name // \"\") | select(test(\"(?i)copilot|claude|devin\")) ] | length > 0"
],
"combinator": "and"
}
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "UPSERT_ENTITY",
"blueprintIdentifier": "githubPullRequest",
"mapping": {
"identifier": "{{ .event.diff.before.payload.headers.Identifier | tostring }}",
"relations": {
"ai_coding_agent": "{{ .event.diff.before.response | [.[] | .commit.author.name // \"\" | if test(\"(?i)copilot\") then \"Copilot\" elif test(\"(?i)claude\") then \"Claude\" elif test(\"(?i)devin\") then \"Devin\" else empty end] | unique }}"
}
}
},
"publish": true
} -
Click
Createto save the automation.
Comments Automation Flow
This flow identifies AI involvement in code review by analyzing comment data.
- Run automation to fetch comments for each PR update.
- Run second automation to extract and identify coding agent names from comments.
Automation 1: Get comments on PR updated
-
Go to the Automations page of your portal.
-
Click on
+ Automation. -
Copy and paste the following JSON schema:
Get comments on PR updated automation (Click to expand)
{
"identifier": "get_comments_on_pr_updated",
"title": "Get Comments on PR Updated",
"description": "Fetch PR comments upon PR updates",
"icon": "GitPullRequest",
"trigger": {
"type": "automation",
"event": {
"type": "ENTITY_UPDATED",
"blueprintIdentifier": "githubPullRequest"
},
"condition": {
"type": "JQ",
"expressions": [
".diff.before.relations.ai_coding_agent == []",
".diff.after.relations.ai_coding_agent == []"
],
"combinator": "and"
}
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "WEBHOOK",
"url": "{{ .event.diff.after.properties.link | sub(\"https://github.com/\"; \"https://api.github.com/repos/\") | sub(\"/pull/\"; \"/issues/\") + \"/comments\" }}",
"agent": false,
"synchronized": true,
"method": "GET",
"headers": {
"Accept": "application/vnd.github+json",
"Authorization": "Bearer {{ .secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}",
"X-GitHub-Api-Version": "2022-11-28",
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Identifier": "{{ .event.context.entityIdentifier | tostring }}"
},
"body": {}
},
"publish": true
} -
Click
Createto save the automation.
Automation 2: Update PR with AI coding agent (comment-based)
This automation only runs if the comments response contains a match for AI agents, ensuring that the PR is updated only when relevant AI activity is detected.
-
Go back to the Automations page of your portal.
-
Click on
+ Automation. -
Copy and paste the following JSON schema:
Update PR with AI coding agent using comments automation (Click to expand)
{
"identifier": "update_pr_with_ai_coding_agent_comment",
"title": "Update PR with AI Coding Agent Using Comments",
"description": "Automation to update the PR with the AI coding agent mentioned in PR comments",
"icon": "GitPullRequest",
"trigger": {
"type": "automation",
"event": {
"type": "RUN_UPDATED",
"actionIdentifier": "get_comments_on_pr_updated"
},
"condition": {
"type": "JQ",
"expressions": [
".diff.after.status == \"SUCCESS\"",
".diff.before.response | [ .[] | ((.user.login // \"\") + \" \" + (.body // \"\")) | select(test(\"(?i)copilot|claude|devin\")) ] | length > 0"
],
"combinator": "and"
}
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "UPSERT_ENTITY",
"blueprintIdentifier": "githubPullRequest",
"mapping": {
"identifier": "{{ .event.diff.before.payload.headers.Identifier | tostring }}",
"relations": {
"ai_coding_agent": "{{ .event.diff.before.response | [.[] | (.user.login // \"\") + \" \" + (.body // \"\") | if test(\"(?i)copilot\") then \"Copilot\" elif test(\"(?i)claude\") then \"Claude\" elif test(\"(?i)devin\") then \"Devin\" else empty end] | unique }}"
}
}
},
"publish": true
} -
Click
Createto save the automation.
Create dashboard
With your data model and automations in place, we can create a dedicated dashboard in Port to visualize all AI-driven pull requests and track their status.
Create AI Control Center dashboard
- Navigate to the Catalog page of your portal.
- Click on the
+ Newbutton in the left sidebar. - Select New dashboard.
- Name the dashboard AI Control Center.
- Input
Track and monitor AI-driven pull requests in your development workflowunder Description. - Select the
AIicon. - Click
Create.
We now have a blank dashboard where we can start adding widgets to visualize insights from AI-driven pull requests.
Add widgets
In the new dashboard, create the following widgets:
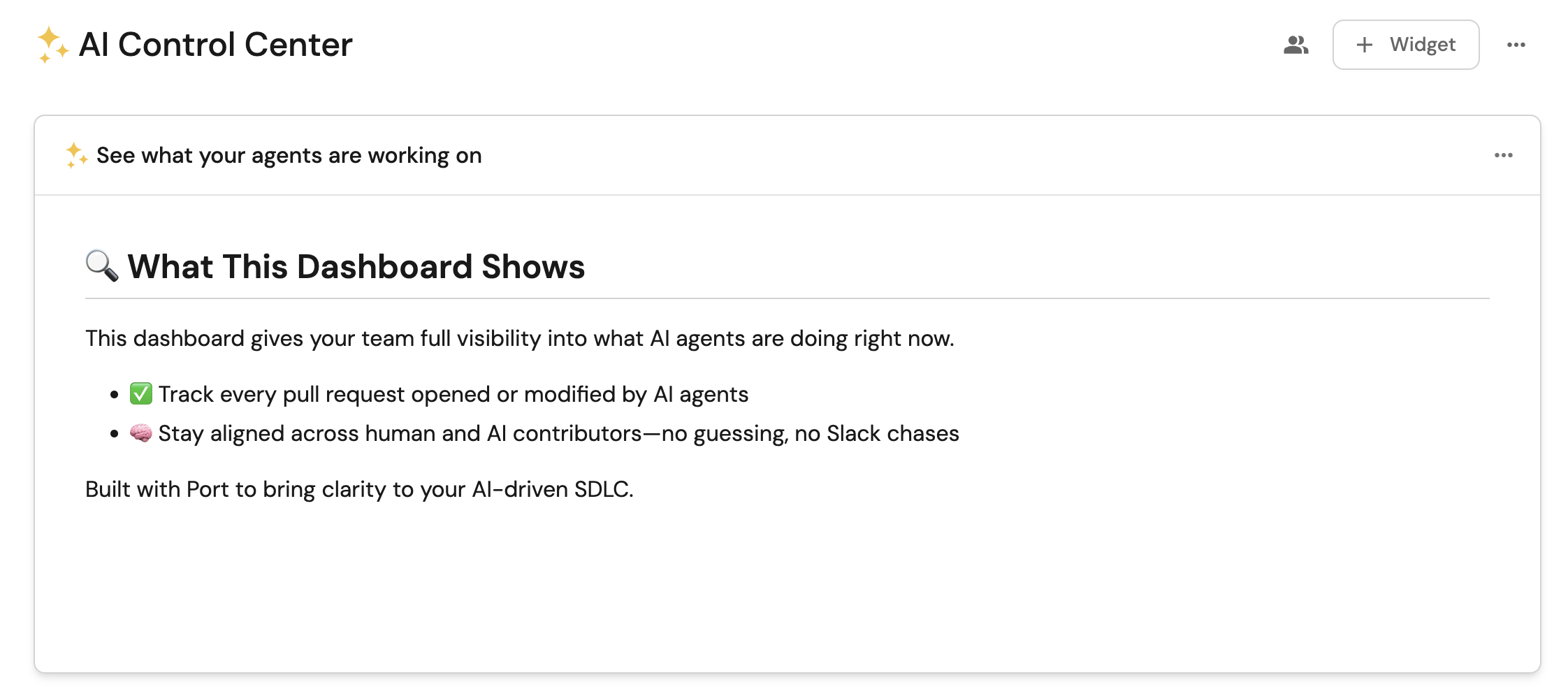
Dashboard description (Click to expand)
- Click
+ Widgetand select Markdown. - Copy and paste the following content:
## 🔍 What This Dashboard Shows
This dashboard gives your team full visibility into what AI agents are doing right now.
- ✅ Track every pull request opened or modified by AI agents
- 🧠 Stay aligned across human and AI contributors—no guessing, no Slack chases
Built with Port to bring clarity to your AI-driven SDLC.
- Click
Save.
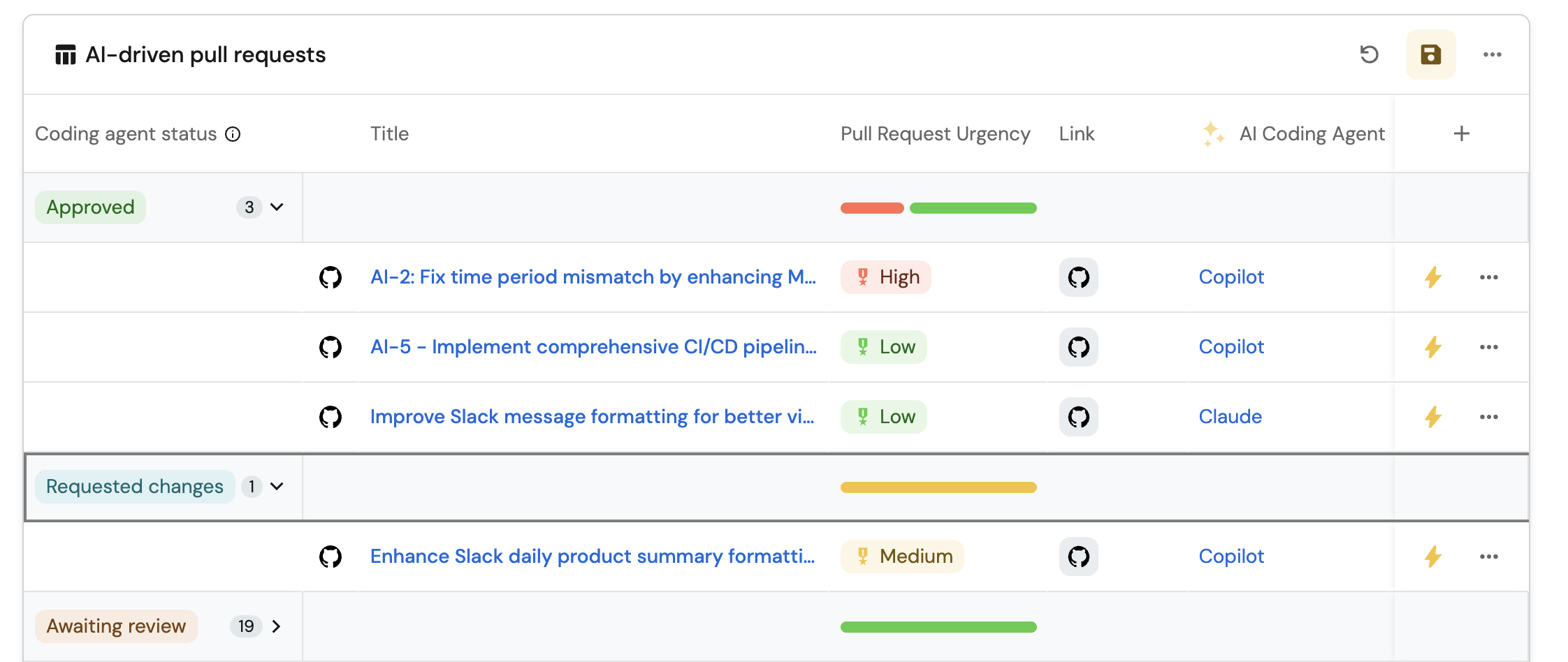
AI-driven pull requests table (Click to expand)
- Click
+ Widgetand select Table. - Title:
AI-driven pull requests(add theGitPullRequesticon). - Choose the Pull Request blueprint.
- Add a filter with the following configuration:
{
"combinator": "or",
"rules": [
{
"blueprint": "ai_coding_agent",
"operator": "relatedTo",
"value": "Claude",
"direction": "downstream"
},
{
"blueprint": "ai_coding_agent",
"operator": "relatedTo",
"value": "Copilot",
"direction": "downstream"
}
]
}
- Click
Saveto add the widget to the dashboard. - Click on the
...button in the top right corner of the table and select Customize table. - In the top right corner of the table, click on
Manage Propertiesand add the following properties:- Title: The title of the pull request.
- Link: The URL to the pull request.
- Repository: The repository where the PR was created.
- AI Coding Agent: The AI agent involved in the PR.
- Click on the Group by option and select Work Status to group PRs by their current status.
- Click on the save icon in the top right corner of the widget to save the customized table.

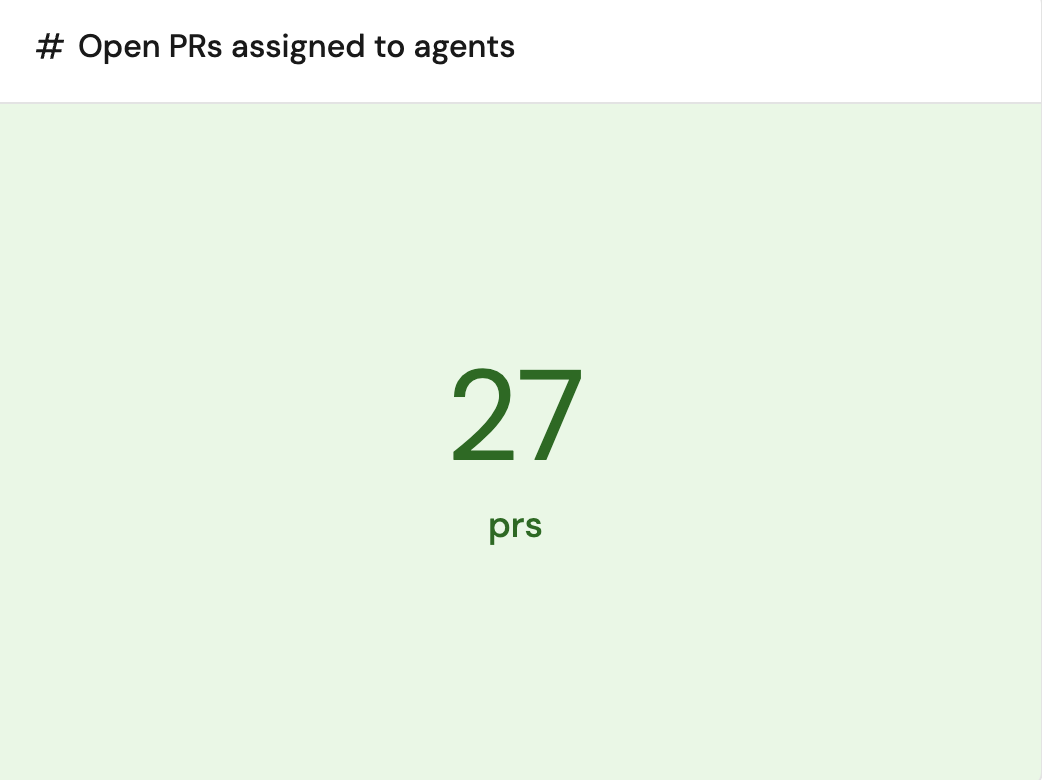
Open PRs assigned to agents (click to expand)
- Click
+ Widgetand select Number Chart. - Title:
Open PRs assigned to agents(add theAIicon). - Select
Aggregate by propertyChart type and choose AI Coding Agent as the Blueprint. - Select
Total open PRsas the Property and choosesumfor the Function. - Select
customas the Unit and inputprsas the Custom unit - Click
Save.
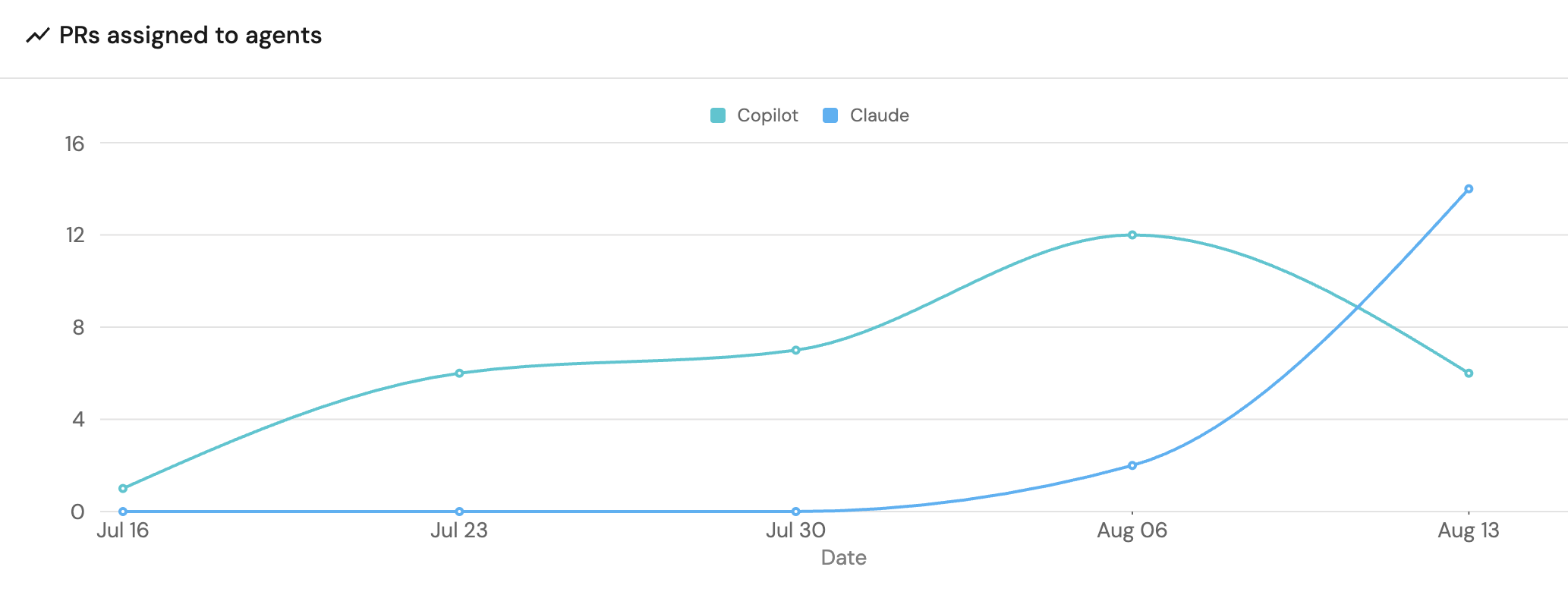
Total PRs assigned to agents (click to expand)
- Click
+ Widgetand select Line Chart. - Title:
PRs assigned to agents, (add theLineCharticon). - Select
Count Entities (All Entities)Chart type and choose Pull Request as the Blueprint. - Input
Total PRsas the Y axis Title and chooseAI Coding Agentas the breakdown Property. - Set
countas the Function. - Input
Dateas the X axis Title and chooseCreated Atas the Measure time by. - Set Time Interval to
Weekand Time Range toIn the past 90 days. - Click
Save.

Test the workflow
Now let us test the complete workflow to ensure everything works correctly.
Trigger a test PR update
- In a repository integrated into Port, trigger a new coding agent to open a pull request.
- Once the PR is opened, verify that it appears in Port and check its AI work status.
- After a new commit is made, ensure the selected coding agent is correctly identified.
Check the dashboard
The AI-driven pull requests should now appear in your AI Control Center dashboard, properly categorized and grouped by work status.