Manage and visualize your ECS tasks
This guide demonstrates how to bring your AWS ECS management experience into Port.
You will learn how to:
- Ingest ECS cluster and service data into Port's software catalog using Port's AWS integration.
- Set up self-service actions to manage ECS services (scale, restart, deploy, health check, rollback, and delete).
- Build dashboards in Port to monitor and take action on your ECS deployments.
Common use cases
- Monitor the health and scaling status of all ECS services across clusters from a single dashboard.
- Quickly scale ECS services up or down based on demand.
- Restart services that are experiencing issues.
- Deploy new container image versions with automated rollback capabilities.
- Run comprehensive health diagnostics and troubleshooting.
- Safely delete services with proper confirmation and cleanup.
Prerequisites
This guide assumes the following:
- You have a Port account and have completed the onboarding process.
- Port's AWS integration is installed in your account.
- You have ECS clusters and services running in your AWS account.
Set up data model
When installing the AWS integration in Port, the AWS Account blueprint is created by default.
However, the ECS Cluster and ECS Service blueprints are not created automatically so we will need to create them manually.
Create the AWS ECS Cluster blueprint
-
Go to the Builder page of your portal.
-
Click on
+ Blueprint. -
Click on the
{...}button in the top right corner, and chooseEdit JSON. -
Add this JSON schema:
AWS ECS Cluster blueprint (click to expand)
{
"identifier": "awsEcsCluster",
"title": "AWS ECS Cluster",
"icon": "AWS",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"link": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Link",
"format": "url",
"description": "AWS Console link to the cluster"
},
"capacityProviders": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Capacity Providers",
"description": "List of capacity providers for the cluster"
},
"activeServicesCount": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Active Services",
"description": "Number of active services in the cluster"
},
"runningTasksCount": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Running Tasks",
"description": "Number of currently running tasks"
},
"pendingTasksCount": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Pending Tasks",
"description": "Number of pending tasks"
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Tags"
},
"arn": {
"type": "string",
"title": "ARN"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"aggregationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
} -
Click
Saveto create the blueprint.
Create the AWS ECS Service blueprint
-
Click on
+ Blueprintagain. -
Click on the
{...}button in the top right corner, and chooseEdit JSON. -
Add this JSON schema:
AWS ECS Service blueprint (click to expand)
{
"identifier": "awsEcsService",
"title": "AWS ECS Service",
"icon": "AWS",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"link": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Link",
"format": "url",
"description": "AWS Console link to the service"
},
"desiredCount": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Desired Count",
"description": "Desired number of tasks for the service"
},
"runningCount": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Running Count",
"description": "Number of tasks currently running"
},
"pendingCount": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Pending Count",
"description": "Number of tasks pending"
},
"taskDefinition": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Task Definition",
"description": "Task definition used by the service"
},
"launchType": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Launch Type",
"enum": ["EC2", "FARGATE", "EXTERNAL"],
"enumColors": {
"EC2": "blue",
"FARGATE": "green",
"EXTERNAL": "orange"
}
},
"status": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Status",
"enum": ["ACTIVE", "DRAINING", "INACTIVE"],
"enumColors": {
"ACTIVE": "green",
"DRAINING": "yellow",
"INACTIVE": "red"
}
},
"schedulingStrategy": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Scheduling Strategy",
"enum": ["REPLICA", "DAEMON"]
},
"platformVersion": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Platform Version"
},
"loadBalancers": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Load Balancers"
},
"arn": {
"type": "string",
"title": "ARN"
},
"enableExecuteCommand": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Enable Execute Command"
},
"healthCheckGracePeriod": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Health Check Grace Prd in sec"
},
"deploymentStrategy": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Deployment Strategy"
},
"maximumPercent": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Maximum Percent"
},
"minimumHealthyPercent": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Minimum Healthy Percent"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {
"healthStatus": {
"title": "Health Status",
"icon": "DefaultProperty",
"calculation": ".properties.runningCount == .properties.desiredCount",
"type": "boolean",
"colorized": true,
"colors": {
"true": "green",
"false": "red"
}
}
},
"aggregationProperties": {},
"relations": {
"cluster": {
"title": "Cluster",
"target": "awsEcsCluster",
"required": false,
"many": false
}
}
} -
Click
Saveto create the blueprint.
Update the mapping configuration
-
Go to the Data Sources page of your portal.
-
Select your AWS integration.
-
Add the following YAML block into the editor to ingest ECS clusters and services:
AWS integration configuration (click to expand)
- kind: AWS::ECS::Cluster
selector:
query: 'true'
useGetResourceAPI: true
port:
entity:
mappings:
identifier: .Properties.Arn
title: .Identifier
blueprint: '"awsEcsCluster"'
properties:
link: '"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=" + .Properties.Arn'
arn: .Properties.Arn
tags: .Properties.Tags
- kind: AWS::ECS::Service
selector:
query: 'true'
port:
entity:
mappings:
identifier: .Properties.ServiceArn
title: .Properties.ServiceName
blueprint: '"awsEcsService"'
properties:
link: '"https://" + .__Region + ".console.aws.amazon.com/ecs/home?region=" + .__Region + "#/clusters/" + .Properties.Cluster + "/services/" + .Properties.ServiceName + "/details"'
desiredCount: .Properties.DesiredCount
runningCount: .Properties.RunningCount // 0
pendingCount: .Properties.PendingCount // 0
taskDefinition: .Properties.TaskDefinition
launchType: .Properties.LaunchType
status: .Properties.Status // "ACTIVE"
schedulingStrategy: .Properties.SchedulingStrategy
platformVersion: .Properties.PlatformVersion
loadBalancers: .Properties.LoadBalancers // []
arn: .Properties.ServiceArn
enableExecuteCommand: .Properties.EnableExecuteCommand
healthCheckGracePeriod: .Properties.HealthCheckGracePeriodSeconds
deploymentStrategy: .Properties.DeploymentConfiguration.Strategy
maximumPercent: .Properties.DeploymentConfiguration.MaximumPercent
minimumHealthyPercent: .Properties.DeploymentConfiguration.MinimumHealthyPercent
relations:
cluster: .Properties.Cluster -
Click
Save & Resyncto apply the mapping.
Set up self-service actions
Now let us create self-service actions to manage your ECS services directly from Port using GitHub Actions.
You will implement workflows to:
-
Scale ECS service tasks up or down.
-
Restart an ECS service.
-
Update task definitions with new container images.
-
Run comprehensive health checks and diagnostics.
-
Rollback deployments to previous versions.
-
Safely delete ECS services.
To implement these use-cases, follow the steps below:
Add GitHub secrets
In your GitHub repository, go to Settings > Secrets and add the following secrets:
PORT_CLIENT_ID- Port Client ID learn more.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET- Port Client Secret learn more.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID- AWS IAM user's access key.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY- AWS IAM user's secret access key.AWS_REGION- AWS region (e.g.,us-east-1).
Ensure your AWS credentials have the permissions to ecs:UpdateService, ecs:DescribeServices, ecs:ListServices, and ecs:DescribeClusters.
Scale ECS Service
Add GitHub workflow
Create the file .github/workflows/scale-ecs-service.yml in the .github/workflows folder of your repository.
We recommend creating a dedicated repository for the workflows that are used by Port actions.
Scale ECS Service GitHub workflow (Click to expand)
name: Scale ECS Service
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
desired_count:
description: 'New desired task count'
required: true
type: number
port_context:
required: true
description: 'Action and general context (blueprint, run id, etc...)'
type: string
jobs:
scale-ecs-service:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Inform Port about workflow start
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: Configuring AWS credentials and scaling ECS service
- name: Configure AWS credentials
uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v4
with:
aws-access-key-id: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
aws-secret-access-key: ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
aws-region: ${{ secrets.AWS_REGION }}
- name: Scale ECS Service
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.cluster }}"
SERVICE_ARN="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}"
echo "Scaling ECS service $SERVICE_ARN in cluster $CLUSTER_NAME to ${{ github.event.inputs.desired_count }} tasks"
aws ecs update-service \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--service "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--desired-count "${{ github.event.inputs.desired_count }}"
- name: Wait for service to stabilize
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.cluster }}"
SERVICE_ARN="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}"
echo "Waiting for service to reach stable state..."
aws ecs wait services-stable \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--services "$SERVICE_ARN"
- name: Inform Port about successful scaling
if: success()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
status: 'SUCCESS'
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: ✅ Successfully scaled ECS service ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }} to ${{ github.event.inputs.desired_count }} tasks
- name: Inform Port about failed scaling
if: failure()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
status: 'FAILURE'
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: ❌ Failed to scale ECS service ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}
Create Port action
-
Go to the Self-service page of your portal.
-
Click on the
+ New Actionbutton. -
Click on the
{...} Edit JSONbutton. -
Copy and paste the following JSON configuration into the editor.
Scale ECS Service action (Click to expand)
Modification RequiredMake sure to replace
<GITHUB_ORG>and<GITHUB_REPO>with your GitHub organization and repository names respectively.{
"identifier": "scale_ecs_service",
"title": "Scale ECS Service",
"icon": "AWS",
"description": "Scale the desired count of tasks for an ECS service",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "DAY-2",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {
"desired_count": {
"title": "Desired Count",
"type": "number",
"description": "Number of tasks to run",
"minimum": 0,
"maximum": 100,
"default": 1
}
},
"required": ["desired_count"],
"order": ["desired_count"]
},
"blueprintIdentifier": "awsEcsService"
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "GITHUB",
"org": "<GITHUB-ORG>",
"repo": "<GITHUB-REPO>",
"workflow": "scale-ecs-service.yml",
"workflowInputs": {
"desired_count": "{{.inputs.\"desired_count\"}}",
"port_context": {
"entity": "{{ .entity }}",
"blueprint": "{{ .action.blueprint }}",
"runId": "{{ .run.id }}",
"trigger": "{{ .trigger }}"
}
},
"reportWorkflowStatus": true
},
"requiredApproval": false
} -
Click
Save.
Now you should see the Scale ECS Service action in the self-service page. 🎉
Restart ECS Service
Add GitHub workflow
Create the file .github/workflows/restart-ecs-service.yml in the .github/workflows folder of your repository.
We recommend creating a dedicated repository for the workflows that are used by Port actions.
Restart ECS Service GitHub workflow (Click to expand)
name: Restart ECS Service
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
port_context:
required: true
description: 'Action and general context (blueprint, run id, etc...)'
type: string
jobs:
restart-ecs-service:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Inform Port about workflow start
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: Configuring AWS credentials and restarting ECS service
- name: Configure AWS credentials
uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v4
with:
aws-access-key-id: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
aws-secret-access-key: ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
aws-region: ${{ secrets.AWS_REGION }}
- name: Force new deployment
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.cluster }}"
SERVICE_ARN="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}"
echo "Forcing new deployment for ECS service $SERVICE_ARN in cluster $CLUSTER_NAME"
aws ecs update-service \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--service "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--force-new-deployment
- name: Wait for deployment to complete
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.cluster }}"
SERVICE_ARN="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}"
echo "Waiting for deployment to complete..."
aws ecs wait services-stable \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--services "$SERVICE_ARN"
- name: Inform Port about successful restart
if: success()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
status: 'SUCCESS'
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: ✅ Successfully restarted ECS service ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}
- name: Inform Port about failed restart
if: failure()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
status: 'FAILURE'
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: ❌ Failed to restart ECS service ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}
Create Port action
-
Go to the Self-service page of your portal.
-
Click on the
+ New Actionbutton. -
Click on the
{...} Edit JSONbutton. -
Copy and paste the following JSON configuration into the editor.
Restart ECS Service action (Click to expand)
Modification RequiredMake sure to replace
<GITHUB_ORG>and<GITHUB_REPO>with your GitHub organization and repository names respectively.{
"identifier": "restart_ecs_service",
"title": "Restart ECS Service",
"icon": "AWS",
"description": "Force a new deployment of the ECS service",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "DAY-2",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {},
"required": [],
"order": []
},
"blueprintIdentifier": "awsEcsService"
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "GITHUB",
"org": "<GITHUB-ORG>",
"repo": "<GITHUB-REPO>",
"workflow": "restart-ecs-service.yml",
"workflowInputs": {
"port_context": {
"entity": "{{ .entity }}",
"blueprint": "{{ .action.blueprint }}",
"runId": "{{ .run.id }}",
"trigger": "{{ .trigger }}"
}
},
"reportWorkflowStatus": true
},
"requiredApproval": false
} -
Click
Save.
Now you should see the Restart ECS Service action in the self-service page. 🎉
Update Task Definition
Add GitHub workflow
Create the file .github/workflows/update-task-definition.yml in the .github/workflows folder of your repository.
We recommend creating a dedicated repository for the workflows that are used by Port actions.
Update Task Definition GitHub workflow (Click to expand)
name: Update ECS Task Definition
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
image_uri:
description: 'New container image URI'
required: true
type: string
port_context:
required: true
description: 'Action and general context (blueprint, run id, etc...)'
type: string
jobs:
update-task-definition:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Inform Port about workflow start
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: Configuring AWS credentials and updating task definition
- name: Configure AWS credentials
uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v4
with:
aws-access-key-id: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
aws-secret-access-key: ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
aws-region: ${{ secrets.AWS_REGION }}
- name: Get current task definition
id: current-task-def
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.cluster }}"
SERVICE_ARN="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}"
# Get current task definition ARN
TASK_DEF_ARN=$(aws ecs describe-services \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--services "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--query 'services[0].taskDefinition' \
--output text)
echo "current_task_def_arn=$TASK_DEF_ARN" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
# Get task definition details
aws ecs describe-task-definition \
--task-definition "$TASK_DEF_ARN" \
--query 'taskDefinition' > current-task-def.json
- name: Update task definition with new image
id: new-task-def
run: |
# Update the image URI in the task definition
jq --arg new_image "${{ github.event.inputs.image_uri }}" \
'.containerDefinitions[0].image = $new_image |
del(.taskDefinitionArn, .revision, .status, .requiresAttributes, .placementConstraints, .compatibilities, .registeredAt, .registeredBy)' \
current-task-def.json > new-task-def.json
# Register new task definition
NEW_TASK_DEF_ARN=$(aws ecs register-task-definition \
--cli-input-json file://new-task-def.json \
--query 'taskDefinition.taskDefinitionArn' \
--output text)
echo "new_task_def_arn=$NEW_TASK_DEF_ARN" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "📝 Registered new task definition: $NEW_TASK_DEF_ARN"
- name: Update service with new task definition
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.cluster }}"
SERVICE_ARN="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}"
NEW_TASK_DEF_ARN="${{ steps.new-task-def.outputs.new_task_def_arn }}"
echo "🚀 Updating service with new task definition..."
aws ecs update-service \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--service "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--task-definition "$NEW_TASK_DEF_ARN"
- name: Wait for deployment to complete
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.cluster }}"
SERVICE_ARN="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}"
echo "⏳ Waiting for deployment to complete..."
aws ecs wait services-stable \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--services "$SERVICE_ARN"
- name: Inform Port about successful update
if: success()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
status: 'SUCCESS'
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: ✅ Successfully updated ECS service ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }} with new image ${{ github.event.inputs.image_uri }}
- name: Inform Port about failed update
if: failure()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
status: 'FAILURE'
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: ❌ Failed to update ECS service ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}
Create Port action
-
Go to the Self-service page of your portal.
-
Click on the
+ New Actionbutton. -
Click on the
{...} Edit JSONbutton. -
Copy and paste the following JSON configuration into the editor.
Update Task Definition action (Click to expand)
Modification RequiredMake sure to replace
<GITHUB_ORG>and<GITHUB_REPO>with your GitHub organization and repository names respectively.{
"identifier": "update_task_definition",
"title": "Update Task Definition",
"icon": "AWS",
"description": "Deploy new container image version",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "DAY-2",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {
"image_uri": {
"title": "Container Image URI",
"type": "string",
"description": "Full URI of the new container image (e.g., account.dkr.ecr.region.amazonaws.com/repo:tag)",
"pattern": "^.+:.+$"
}
},
"required": ["image_uri"],
"order": ["image_uri"]
},
"blueprintIdentifier": "awsEcsService"
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "GITHUB",
"org": "<GITHUB-ORG>",
"repo": "<GITHUB-REPO>",
"workflow": "update-task-definition.yml",
"workflowInputs": {
"image_uri": "{{.inputs.\"image_uri\"}}",
"port_context": {
"entity": "{{ .entity }}",
"blueprint": "{{ .action.blueprint }}",
"runId": "{{ .run.id }}",
"trigger": "{{ .trigger }}"
}
},
"reportWorkflowStatus": true
},
"requiredApproval": false
} -
Click
Save.
Now you should see the Update Task Definition action in the self-service page. 🎉
Service Health Check
Add GitHub workflow
Create the file .github/workflows/service-health-check.yml in the .github/workflows folder of your repository.
We recommend creating a dedicated repository for the workflows that are used by Port actions.
Service Health Check GitHub workflow (Click to expand)
name: ECS Service Health Check
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
port_context:
required: true
description: 'Action and general context (blueprint, run id, etc...)'
type: string
jobs:
health-check:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Inform Port about workflow start
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: Running health check on ECS service
- name: Configure AWS credentials
uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v4
with:
aws-access-key-id: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
aws-secret-access-key: ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
aws-region: ${{ secrets.AWS_REGION }}
- name: Get service details
id: service-details
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.cluster }}"
SERVICE_ARN="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}"
echo "🔍 Checking service health for $SERVICE_ARN in cluster $CLUSTER_NAME"
# Get service details
aws ecs describe-services \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--services "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--output table
# Store service status for later use
SERVICE_STATUS=$(aws ecs describe-services \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--services "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--query 'services[0].status' \
--output text)
RUNNING_COUNT=$(aws ecs describe-services \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--services "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--query 'services[0].runningCount' \
--output text)
DESIRED_COUNT=$(aws ecs describe-services \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--services "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--query 'services[0].desiredCount' \
--output text)
echo "service_status=$SERVICE_STATUS" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "running_count=$RUNNING_COUNT" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "desired_count=$DESIRED_COUNT" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
- name: Check running tasks
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.cluster }}"
SERVICE_ARN="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}"
echo "📋 Listing running tasks..."
# List tasks for the service
aws ecs list-tasks \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--service-name "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--output table
# Get task details if tasks exist
TASK_ARNS=$(aws ecs list-tasks \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--service-name "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--query 'taskArns' \
--output text)
if [ "$TASK_ARNS" != "None" ] && [ -n "$TASK_ARNS" ]; then
echo "🔍 Task details:"
aws ecs describe-tasks \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--tasks $TASK_ARNS \
--output table
else
echo "⚠️ No running tasks found"
fi
- name: Check service events
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.cluster }}"
SERVICE_ARN="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}"
echo "📅 Recent service events:"
aws ecs describe-services \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--services "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--query 'services[0].events[:10]' \
--output table
- name: Health summary
run: |
SERVICE_STATUS="${{ steps.service-details.outputs.service_status }}"
RUNNING_COUNT="${{ steps.service-details.outputs.running_count }}"
DESIRED_COUNT="${{ steps.service-details.outputs.desired_count }}"
echo "📊 Health Summary:"
echo "==================="
echo "Service Status: $SERVICE_STATUS"
echo "Running Tasks: $RUNNING_COUNT"
echo "Desired Tasks: $DESIRED_COUNT"
if [ "$SERVICE_STATUS" = "ACTIVE" ] && [ "$RUNNING_COUNT" = "$DESIRED_COUNT" ]; then
echo "✅ Service is healthy"
HEALTH_STATUS="HEALTHY"
else
echo "⚠️ Service needs attention"
HEALTH_STATUS="UNHEALTHY"
fi
echo "health_status=$HEALTH_STATUS" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
- name: Inform Port about health check results
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
status: 'SUCCESS'
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: |
🏥 Health Check Complete
Status: ${{ steps.service-details.outputs.service_status }}
Running: ${{ steps.service-details.outputs.running_count }}/${{ steps.service-details.outputs.desired_count }} tasks
- name: Inform Port about health check failure
if: failure()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
status: 'FAILURE'
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: ❌ Health check failed for ECS service ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}
Create Port action
-
Go to the Self-service page of your portal.
-
Click on the
+ New Actionbutton. -
Click on the
{...} Edit JSONbutton. -
Copy and paste the following JSON configuration into the editor.
Service Health Check action (Click to expand)
Modification RequiredMake sure to replace
<GITHUB_ORG>and<GITHUB_REPO>with your GitHub organization and repository names respectively.{
"identifier": "service_health_check",
"title": "Service Health Check",
"icon": "DefaultProperty",
"description": "Run diagnostics on service health and check task status",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "DAY-2",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {},
"required": [],
"order": []
},
"blueprintIdentifier": "awsEcsService"
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "GITHUB",
"org": "<GITHUB-ORG>",
"repo": "<GITHUB-REPO>",
"workflow": "service-health-check.yml",
"workflowInputs": {
"port_context": {
"entity": "{{ .entity }}",
"blueprint": "{{ .action.blueprint }}",
"runId": "{{ .run.id }}",
"trigger": "{{ .trigger }}"
}
},
"reportWorkflowStatus": true
},
"requiredApproval": false
} -
Click
Save.
Now you should see the Service Health Check action in the self-service page. 🎉
Rollback Deployment
Add GitHub workflow
Create the file .github/workflows/rollback-deployment.yml in the .github/workflows folder of your repository.
We recommend creating a dedicated repository for the workflows that are used by Port actions.
Rollback Deployment GitHub workflow (Click to expand)
name: Rollback ECS Deployment
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
port_context:
required: true
description: 'Action and general context (blueprint, run id, etc...)'
type: string
jobs:
rollback-deployment:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Inform Port about workflow start
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: Initiating rollback for ECS service
- name: Configure AWS credentials
uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v4
with:
aws-access-key-id: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
aws-secret-access-key: ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
aws-region: ${{ secrets.AWS_REGION }}
- name: Get current and previous task definitions
id: task-definitions
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.cluster }}"
SERVICE_ARN="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}"
# Get current task definition
CURRENT_TASK_DEF=$(aws ecs describe-services \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--services "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--query 'services[0].taskDefinition' \
--output text)
echo "current_task_def=$CURRENT_TASK_DEF" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "📋 Current task definition: $CURRENT_TASK_DEF"
# Extract family name and current revision
FAMILY_NAME=$(echo $CURRENT_TASK_DEF | sed 's/.*task-definition\/\([^:]*\):.*/\1/')
CURRENT_REVISION=$(echo $CURRENT_TASK_DEF | sed 's/.*://')
echo "family_name=$FAMILY_NAME" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "current_revision=$CURRENT_REVISION" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
# Calculate previous revision
PREVIOUS_REVISION=$((CURRENT_REVISION - 1))
if [ $PREVIOUS_REVISION -lt 1 ]; then
echo "❌ No previous revision available to rollback to"
exit 1
fi
PREVIOUS_TASK_DEF="$FAMILY_NAME:$PREVIOUS_REVISION"
echo "previous_task_def=$PREVIOUS_TASK_DEF" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "🔄 Will rollback to: $PREVIOUS_TASK_DEF"
# Verify previous task definition exists
if ! aws ecs describe-task-definition --task-definition "$PREVIOUS_TASK_DEF" > /dev/null 2>&1; then
echo "❌ Previous task definition $PREVIOUS_TASK_DEF does not exist"
exit 1
fi
- name: Perform rollback
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.cluster }}"
SERVICE_ARN="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}"
PREVIOUS_TASK_DEF="${{ steps.task-definitions.outputs.previous_task_def }}"
echo "🔄 Rolling back service to previous task definition..."
aws ecs update-service \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--service "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--task-definition "$PREVIOUS_TASK_DEF"
echo "✅ Rollback initiated"
- name: Wait for rollback to complete
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.cluster }}"
SERVICE_ARN="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}"
echo "⏳ Waiting for rollback deployment to stabilize..."
# Wait for service to become stable
aws ecs wait services-stable \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--services "$SERVICE_ARN"
echo "✅ Rollback completed successfully"
- name: Verify rollback
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.cluster }}"
SERVICE_ARN="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}"
EXPECTED_TASK_DEF="${{ steps.task-definitions.outputs.previous_task_def }}"
# Verify the service is now using the previous task definition
CURRENT_TASK_DEF=$(aws ecs describe-services \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--services "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--query 'services[0].taskDefinition' \
--output text)
CURRENT_FAMILY_REV=$(echo $CURRENT_TASK_DEF | sed 's/.*task-definition\/\(.*\)/\1/')
if [[ "$CURRENT_FAMILY_REV" == "$EXPECTED_TASK_DEF" ]]; then
echo "✅ Rollback verification successful"
echo "Service is now running: $CURRENT_TASK_DEF"
else
echo "❌ Rollback verification failed"
echo "Expected: $EXPECTED_TASK_DEF"
echo "Actual: $CURRENT_FAMILY_REV"
exit 1
fi
- name: Inform Port about successful rollback
if: success()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
status: 'SUCCESS'
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: |
✅ Rollback completed successfully
Rolled back from: ${{ steps.task-definitions.outputs.current_task_def }}
Rolled back to: ${{ steps.task-definitions.outputs.previous_task_def }}
- name: Inform Port about failed rollback
if: failure()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
status: 'FAILURE'
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: ❌ Failed to rollback ECS service ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}
Create Port action
-
Go to the Self-service page of your portal.
-
Click on the
+ New Actionbutton. -
Click on the
{...} Edit JSONbutton. -
Copy and paste the following JSON configuration into the editor.
Rollback Deployment action (Click to expand)
Modification RequiredMake sure to replace
<GITHUB_ORG>and<GITHUB_REPO>with your GitHub organization and repository names respectively.{
"identifier": "rollback_deployment",
"title": "Rollback Deployment",
"icon": "AWS",
"description": "Revert to previous task definition revision",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "DAY-2",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {},
"required": [],
"order": []
},
"blueprintIdentifier": "awsEcsService"
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "GITHUB",
"org": "<GITHUB-ORG>",
"repo": "<GITHUB-REPO>",
"workflow": "rollback-deployment.yml",
"workflowInputs": {
"port_context": {
"entity": "{{ .entity }}",
"blueprint": "{{ .action.blueprint }}",
"runId": "{{ .run.id }}",
"trigger": "{{ .trigger }}"
}
},
"reportWorkflowStatus": true
},
"requiredApproval": true
} -
Click
Save.
Now you should see the Rollback Deployment action in the self-service page. 🎉
Note that the rollback action has requiredApproval: true set for safety, as rollbacks can have significant impact on production services.
Delete ECS Service
Add GitHub workflow
Create the file .github/workflows/delete-ecs-service.yml in the .github/workflows folder of your repository.
We recommend creating a dedicated repository for the workflows that are used by Port actions.
Delete ECS Service GitHub workflow (Click to expand)
name: Delete ECS Service
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
confirmation:
description: 'Type DELETE to confirm service deletion'
required: true
type: string
port_context:
required: true
description: 'Action and general context (blueprint, run id, etc...)'
type: string
jobs:
delete-ecs-service:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Validate confirmation
run: |
if [ "${{ github.event.inputs.confirmation }}" != "DELETE" ]; then
echo "❌ Confirmation failed. You must type 'DELETE' exactly to proceed."
exit 1
fi
echo "✅ Confirmation validated"
- name: Inform Port about workflow start
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: ⚠️ Initiating ECS service deletion
- name: Configure AWS credentials
uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v4
with:
aws-access-key-id: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
aws-secret-access-key: ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
aws-region: ${{ secrets.AWS_REGION }}
- name: Get service information
id: service-info
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.cluster }}"
SERVICE_ARN="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}"
echo "🔍 Getting service information..."
# Get service details before deletion
SERVICE_NAME=$(aws ecs describe-services \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--services "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--query 'services[0].serviceName' \
--output text)
DESIRED_COUNT=$(aws ecs describe-services \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--services "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--query 'services[0].desiredCount' \
--output text)
RUNNING_COUNT=$(aws ecs describe-services \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--services "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--query 'services[0].runningCount' \
--output text)
TASK_DEFINITION=$(aws ecs describe-services \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--services "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--query 'services[0].taskDefinition' \
--output text)
echo "service_name=$SERVICE_NAME" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "desired_count=$DESIRED_COUNT" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "running_count=$RUNNING_COUNT" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "task_definition=$TASK_DEFINITION" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "📋 Service Details:"
echo " Name: $SERVICE_NAME"
echo " Desired Count: $DESIRED_COUNT"
echo " Running Count: $RUNNING_COUNT"
echo " Task Definition: $TASK_DEFINITION"
- name: Scale service to zero
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.cluster }}"
SERVICE_ARN="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}"
echo "⬇️ Scaling service to 0 tasks before deletion..."
aws ecs update-service \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--service "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--desired-count 0
echo "✅ Service scaled to 0 tasks"
- name: Wait for tasks to stop
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.cluster }}"
SERVICE_ARN="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}"
echo "⏳ Waiting for all tasks to stop..."
# Wait for service to become stable with 0 running tasks
aws ecs wait services-stable \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--services "$SERVICE_ARN"
# Verify no tasks are running
RUNNING_COUNT=$(aws ecs describe-services \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--services "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--query 'services[0].runningCount' \
--output text)
if [ "$RUNNING_COUNT" -eq 0 ]; then
echo "✅ All tasks have stopped"
else
echo "⚠️ Warning: $RUNNING_COUNT tasks still running"
fi
- name: Delete the service
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.cluster }}"
SERVICE_ARN="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}"
echo "🗑️ Deleting ECS service..."
aws ecs delete-service \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--service "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--force
echo "✅ Service deletion initiated"
- name: Wait for service deletion
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.cluster }}"
SERVICE_ARN="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}"
echo "⏳ Waiting for service deletion to complete..."
# Wait for service to be deleted (this can take a few minutes)
aws ecs wait services-inactive \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--services "$SERVICE_ARN"
echo "✅ Service successfully deleted"
- name: Verify deletion
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.cluster }}"
SERVICE_ARN="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}"
echo "🔍 Verifying service deletion..."
# Check if service still exists
SERVICE_STATUS=$(aws ecs describe-services \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--services "$SERVICE_ARN" \
--query 'services[0].status' \
--output text 2>/dev/null || echo "NOT_FOUND")
if [ "$SERVICE_STATUS" = "INACTIVE" ] || [ "$SERVICE_STATUS" = "NOT_FOUND" ]; then
echo "✅ Service deletion verified"
else
echo "❌ Service deletion verification failed. Status: $SERVICE_STATUS"
exit 1
fi
- name: Delete Port entity
run: |
SERVICE_ARN="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}"
echo "🗑️ Deleting corresponding Port entity..."
curl -X DELETE \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $(curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"clientId": "${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}", "clientSecret": "${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}"}' \
https://api.getport.io/v1/auth/access_token | jq -r '.accessToken')" \
"https://api.getport.io/v1/blueprints/awsEcsService/entities/$(echo '$SERVICE_ARN' | sed 's/[\/:]/%2F/g')"
echo "✅ Port entity deletion requested"
- name: Inform Port about successful deletion
if: success()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
status: 'SUCCESS'
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: |
✅ ECS Service Successfully Deleted
Service: ${{ steps.service-info.outputs.service_name }}
Previous Desired Count: ${{ steps.service-info.outputs.desired_count }}
Task Definition: ${{ steps.service-info.outputs.task_definition }}
- name: Inform Port about failed deletion
if: failure()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
status: 'FAILURE'
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: ❌ Failed to delete ECS service ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }}
Create Port action
-
Go to the Self-service page of your portal.
-
Click on the
+ New Actionbutton. -
Click on the
{...} Edit JSONbutton. -
Copy and paste the following JSON configuration into the editor.
Delete ECS Service action (Click to expand)
Modification RequiredMake sure to replace
<GITHUB_ORG>and<GITHUB_REPO>with your GitHub organization and repository names respectively.{
"identifier": "delete_ecs_service",
"title": "Delete ECS Service",
"icon": "AWS",
"description": "Permanently delete an ECS service",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "DELETE",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {
"confirmation": {
"title": "Confirmation",
"type": "string",
"description": "Type 'DELETE' to confirm permanent deletion",
"pattern": "^DELETE$"
}
},
"required": ["confirmation"],
"order": ["confirmation"]
},
"blueprintIdentifier": "awsEcsService"
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "GITHUB",
"org": "<GITHUB-ORG>",
"repo": "<GITHUB-REPO>",
"workflow": "delete-ecs-service.yml",
"workflowInputs": {
"confirmation": "{{.inputs.\"confirmation\"}}",
"port_context": {
"entity": "{{ .entity }}",
"blueprint": "{{ .action.blueprint }}",
"runId": "{{ .run.id }}",
"trigger": "{{ .trigger }}"
}
},
"reportWorkflowStatus": true
},
"requiredApproval": true
} -
Click
Save.
Now you should see the Delete ECS Service action in the self-service page. 🎉
The delete service action includes multiple safety measures:
- Double confirmation: Requires typing "DELETE" exactly
- Manual approval:
requiredApproval: true - Graceful shutdown: Scales to 0 before deletion
- Verification: Confirms deletion completed
- Port cleanup: Removes the entity from Port catalog
Let's test it!
Now that you have set up all the self-service actions, let's test them to ensure they work correctly with your ECS services.
-
Head to the self-service page of your portal.
-
Click on the
Service Health Checkaction.- Choose any ECS service from your catalog.
- Click on
Execute. - Verify the health summary provides useful insights about your service.
-
Scale ECS Service
- Click on the
Scale ECS Serviceaction. - Choose an ECS service that currently has running tasks.
- Enter a different desired count (e.g., if it has 2 tasks, try 3 or 1).
- Click on
Execute. - Wait for the scaling operation to complete.
- Verify in the AWS Console that the service now has the new desired count.
- Click on the
-
Update Task Definition
- Click on the
Update Task Definitionaction. - Choose an ECS service to update.
- Enter a new container image URI. Some examples:
- If currently using
nginx:1.24, trynginx:1.25 - If using a custom image, try a different tag like
:v2.0
- If currently using
- Click on
Execute.
- Click on the
-
Restart ECS Service
- Click on the
Restart ECS Serviceaction. - Choose an ECS service to restart.
- Click on
Execute.
- Click on the
-
Rollback Deployment
- Click on the
Rollback Deploymentaction. - Choose an ECS service that has been updated at least once.
- Click on
Execute. - Approve the action when prompted (due to
requiredApproval: true). - Monitor the rollback process:
- Previous task definition identified
- Service updated to previous revision
- Deployment completion verification
- Click on the
-
Delete ECS Service
- Click on the
Delete ECS Serviceaction. - Choose a test service that can be safely deleted.
- Type
DELETEexactly in the confirmation field. - Click on
Execute. - Approve the action when prompted.
- Monitor the deletion process:
- Service information captured
- Scaling to 0 tasks
- Service deletion
- Verification of removal
- Click on the
Visualize metrics
With your data and actions in place, we can create a dedicated dashboard in Port to visualize all ECS services by state, launch type, or cluster using customizable widgets. In addition, we can trigger actions (scale, restart) directly from the dashboard.
Create a dashboard
-
Navigate to the Catalog page of your portal.
-
Click on the
+ Newbutton in the left sidebar. -
Select New dashboard.
-
Name the dashboard ECS Management.
-
Input
Scale and restart your AWS ECS servicesunder Description. -
Select the
AWSicon. -
Click
Create.
We now have a blank dashboard where we can start adding widgets to visualize insights from our AWS ECS.
Add widgets
In the new dashboard, create the following widgets:
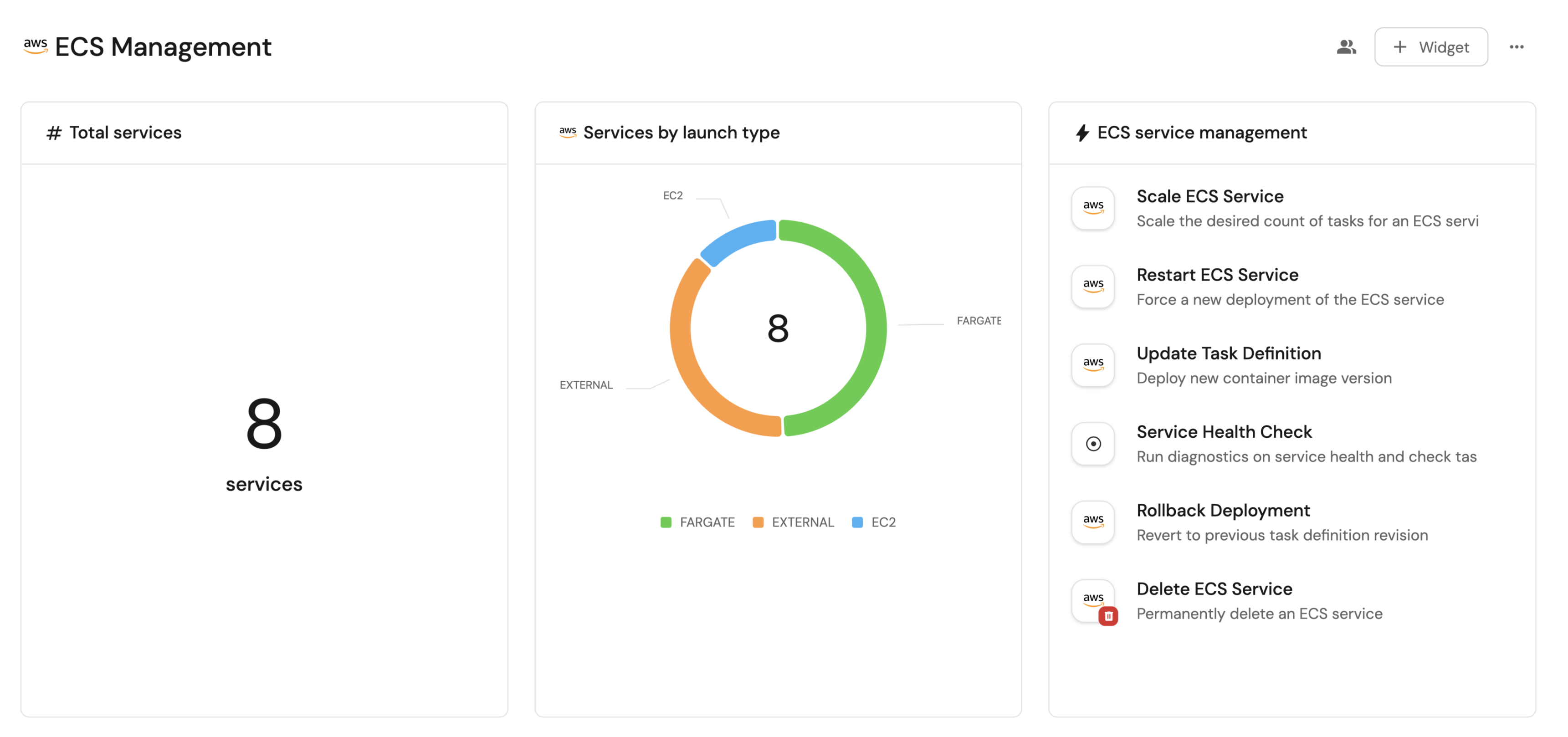
Total ECS services (click to expand)
-
Click
+ Widgetand select Number Chart. -
Title:
Total services(add theAWSicon). -
Select
Count entitiesChart type and choose AWS ECS Service as the Blueprint. -
Select
countfor the Function. -
Select
customas the Unit and inputservicesas the Custom unit -
Click
Save.
Services by launch type (click to expand)
-
Click
+ Widgetand select Pie chart. -
Title:
Services by launch type(add theAWSicon). -
Choose the AWS ECS Service blueprint.
-
Under
Breakdown by property, select the Launch Type property -
Click Save.
Service health status (click to expand)
-
Click
+ Widgetand select Pie chart. -
Title:
Service health status(add theDefaultPropertyicon). -
Choose the AWS ECS Service blueprint.
-
Under
Breakdown by property, select the Health Status property -
Click Save.
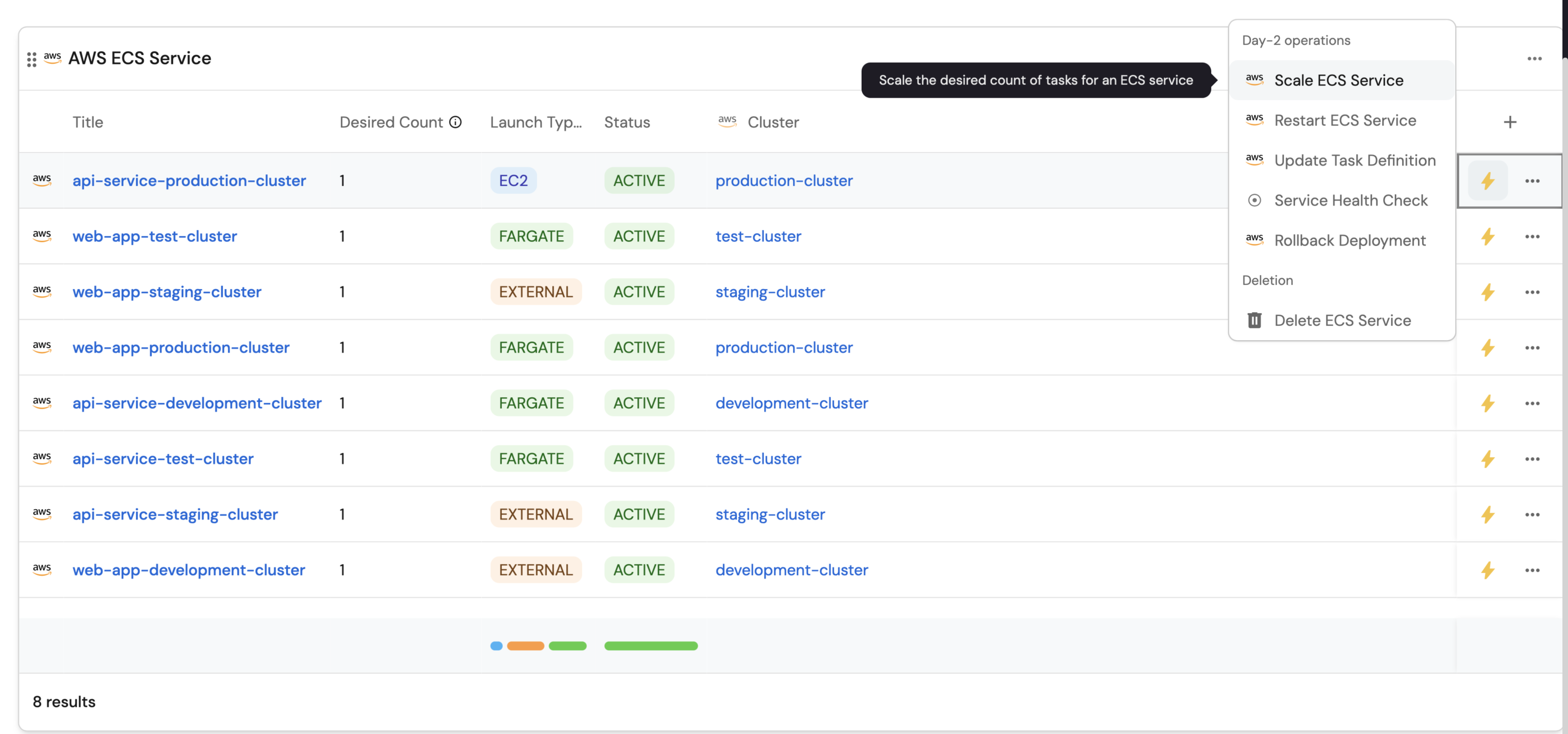
ECS services view (click to expand)
-
Click
+ Widgetand select Table. -
Title the widget All Services.
-
Choose the AWS ECS Service blueprint
-
Click Save to add the widget to the dashboard.
-
Click on the
...button in the top right corner of the table and select Customize table. -
In the top right corner of the table, click on
Manage Propertiesand add the following properties:- Status: The current status of the service.
- Desired Count: Target number of tasks.
- Launch Type: How tasks are launched.
- Cluster: Related ECS cluster.
-
Click on the save icon in the top right corner of the widget to save the customized table.
Task count distribution (click to expand)
-
Click
+ Widgetand select Number Chart. -
Title:
Total running tasks(add theDefaultPropertyicon). -
Choose the AWS ECS Service blueprint.
-
Select
countas the Aggregation function. -
Under
Measure property, select the Running Count property. -
Select
customas the Unit and inputtasksas the Custom unit. -
Click Save.
Platform version overview (click to expand)
-
Click
+ Widgetand select Pie chart. -
Title:
Platform versions(add theDefaultPropertyicon). -
Choose the AWS ECS Service blueprint.
-
Under
Breakdown by property, select the Platform Version property. -
Click Save.
ECS management actions (click to expand)
-
Click
+ Widgetand select Action Card. -
Title:
ECS service management(add theAWSicon). -
Choose the AWS ECS Service blueprint.
-
Under
Actions, select all the ECS management actions we created:- Scale ECS Service
- Restart ECS Service
- Update Task Definition
- Service Health Check
- Rollback Deployment
- Delete ECS Service
-
Click Save.