Auto-assign bugs to owners with AI
Jira bugs often lack clear ownership, which slows triage and creates inconsistent routing. With Port's catalog, automations, and AI agents, you can detect new Jira bugs, resolve ownership from your service and team data, and update Jira with the right assignee and reasoning. This guide helps you reduce manual triage time, improve accountability, and route bugs to the teams best positioned to fix them.
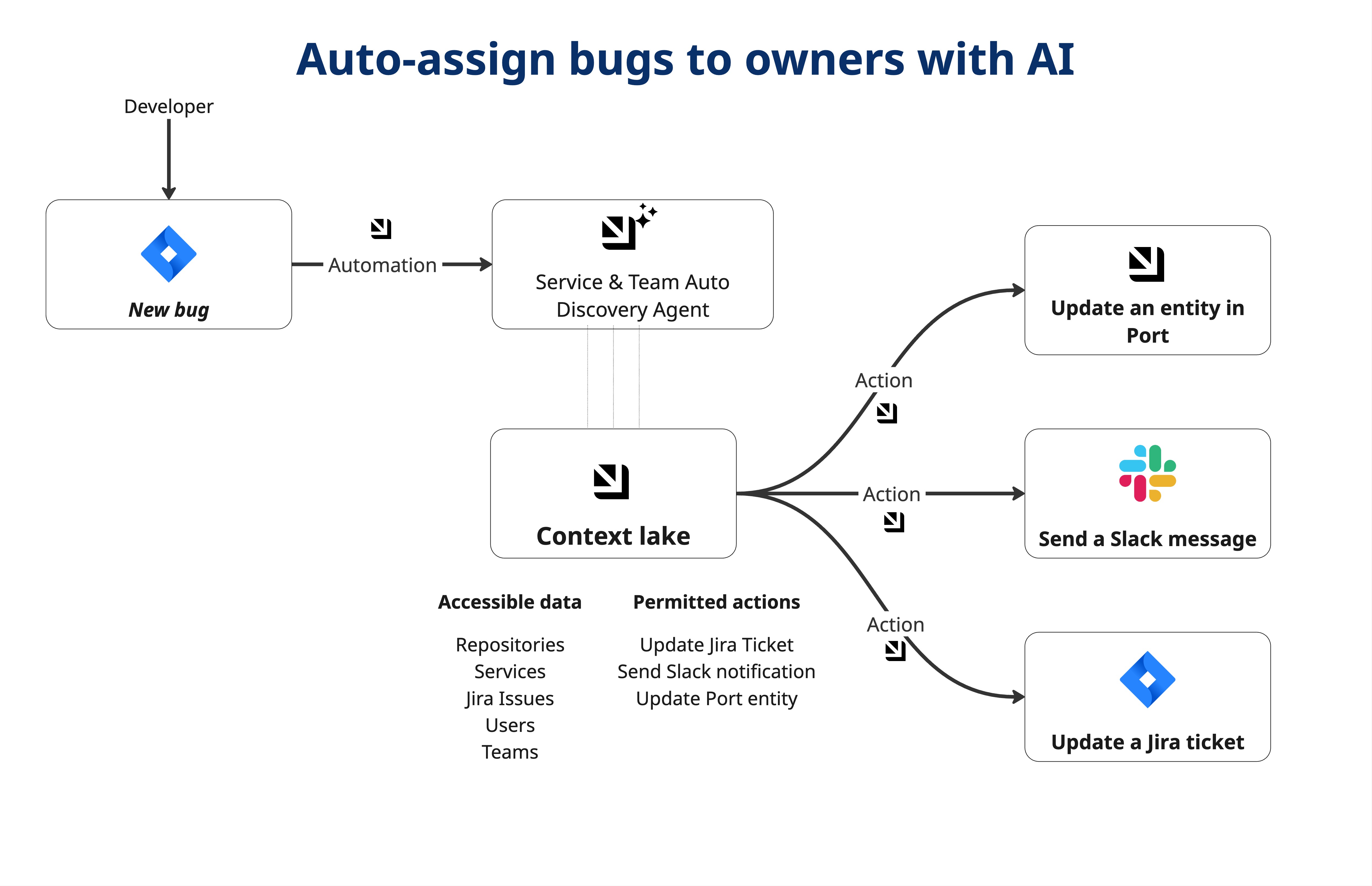
Common use cases
- Reduce manual triage time by assigning new bugs automatically.
- Improve ownership consistency with service and team mappings in Port.
- Surface unowned bugs early with labels, comments, and Slack alerts.
Prerequisites
This guide assumes the following:
- You have a Port account and have completed the onboarding process.
- You have service and team entities in your catalog, and each service has an owning team. If you need help, see relate blueprints.
- You have access to a Jira instance with API access and can create an API token.
- Port's Jira integration is installed in your account.
- You have access to a Slack developer account with permissions to create apps.
- You can create and configure AI agents in Port.
Set up data model
You will configure the Jira blueprints and relations that the automation relies on. The examples below assume you are extending the data model that Port's Jira Ocean integration creates.
Jira user blueprint
-
Go to the builder page of your portal.
-
Click + Blueprint.
-
Click
{...} Edit JSON. -
Paste the JSON below:
Jira user blueprint (click to expand)
{
"identifier": "jiraUser",
"description": "A Jira user account",
"title": "Jira User",
"icon": "Jira",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"emailAddress": {
"title": "Email",
"type": "string",
"format": "email",
"description": "User's email address"
},
"displayName": {
"title": "Display Name",
"type": "string",
"description": "User's full name as displayed in Jira"
},
"active": {
"title": "Active Status",
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether the user account is active"
},
"accountType": {
"title": "Account Type",
"type": "string",
"description": "Type of Jira account (e.g., atlassian, customer)"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"aggregationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
} -
Click Create to save the blueprint.
Jira project blueprint
-
Go to the builder page of your portal.
-
Click + Blueprint.
-
Click
{...} Edit JSON. -
Paste the JSON below:
Jira project blueprint (click to expand)
{
"identifier": "jiraProject",
"description": "A Jira project",
"title": "Jira Project",
"icon": "Jira",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"url": {
"title": "Project URL",
"type": "string",
"format": "url",
"description": "URL to the project in Jira"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"aggregationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
} -
Click Create to save the blueprint.
Jira issue blueprint
This blueprint stores issue data and relationships that power assignment logic.
-
Go to the builder page of your portal.
-
Click + Blueprint.
-
Click
{...} Edit JSON. -
Paste the JSON below:
Jira issue blueprint (click to expand)
{
"identifier": "jiraIssue",
"title": "Jira Issue",
"icon": "Jira",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"url": {
"title": "Issue URL",
"type": "string",
"format": "url",
"description": "URL to the issue in Jira"
},
"status": {
"title": "Status",
"type": "string",
"description": "The status of the issue"
},
"issueType": {
"title": "Type",
"type": "string",
"description": "The type of the issue"
},
"components": {
"title": "Components",
"type": "string",
"description": "The Jira component value"
},
"creator": {
"title": "Creator",
"type": "string",
"description": "The user that created to the issue",
"format": "user"
},
"priority": {
"title": "Priority",
"type": "string",
"description": "The priority of the issue"
},
"labels": {
"items": {
"type": "string"
},
"title": "Labels",
"type": "array"
},
"created": {
"title": "Created At",
"type": "string",
"description": "The created datetime of the issue",
"format": "date-time"
},
"updated": {
"title": "Updated At",
"type": "string",
"description": "The updated datetime of the issue",
"format": "date-time"
},
"resolutionDate": {
"title": "Resolved At",
"type": "string",
"description": "The datetime the issue changed to a resolved state",
"format": "date-time"
},
"description": {
"icon": "DefaultProperty",
"type": "string",
"title": "Description",
"format": "markdown"
},
"ai_assignment_reasoning": {
"icon": "DefaultProperty",
"type": "string",
"title": "AI Assignment Reasoning"
},
"assignment_source": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Ownership Assignment Source"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {
"handlingDuration": {
"title": "Handling Duration (Days)",
"icon": "Clock",
"description": "The amount of time in days from issue creation to issue resolution",
"calculation": "if (.properties.resolutionDate != null and .properties.created != null) then ((.properties.resolutionDate[0:19] + \"Z\" | fromdateiso8601) - (.properties.created[0:19] + \"Z\" | fromdateiso8601)) / 86400 else null end",
"type": "number"
}
},
"aggregationProperties": {},
"relations": {
"subtasks": {
"title": "Subtasks",
"target": "jiraIssue",
"required": false,
"many": true
},
"ai_discovered_service": {
"title": "AI Discovered Service",
"target": "service",
"required": false,
"many": false
},
"ai_discovered_team": {
"title": "AI Discovered Team",
"target": "_team",
"required": false,
"many": false
},
"reporter": {
"title": "Reporter",
"target": "_user",
"required": false,
"many": false
},
"assignee": {
"title": "Assignee",
"target": "_user",
"required": false,
"many": false
},
"parentIssue": {
"title": "Parent Issue",
"target": "jiraIssue",
"required": false,
"many": false
},
"project": {
"title": "Project",
"description": "The Jira project that contains this issue",
"target": "jiraProject",
"required": false,
"many": false
},
"jira_user_reporter": {
"title": "Reporter (Jira User)",
"target": "jiraUser",
"required": false,
"many": false
},
"jira_user_assignee": {
"title": "Assignee (Jira User)",
"target": "jiraUser",
"required": false,
"many": false
}
}
} -
Click Create to save the blueprint.
Update the integration mapping
- Go to the data sources page of your portal.
- Select the Jira integration.
- Add the following YAML block into the editor:
Jira integration mapping (click to expand)
deleteDependentEntities: true
createMissingRelatedEntities: true
enableMergeEntity: true
resources:
- kind: user
selector:
query: 'true'
port:
entity:
mappings:
identifier: .accountId
title: .displayName
blueprint: '"jiraUser"'
properties:
emailAddress: .emailAddress
displayName: .displayName
active: .active
accountType: .accountType
- kind: project
selector:
query: 'true'
port:
entity:
mappings:
identifier: .key
title: .name
blueprint: '"jiraProject"'
properties:
url: (.self | split("/") | .[:3] | join("/")) + "/projects/" + .key
- kind: issue
selector:
query: 'true'
jql: (statusCategory != Done) OR (created >= -1w) OR (updated >= -1w)
port:
entity:
mappings:
identifier: .key
title: .fields.summary
blueprint: '"jiraIssue"'
properties:
url: (.self | split("/") | .[:3] | join("/")) + "/browse/" + .key
status: .fields.status.name
issueType: .fields.issuetype.name
components: .fields.customfield_10308.value
creator: .fields.creator.emailAddress
priority: .fields.priority.name
labels: .fields.labels
created: .fields.created
updated: .fields.updated
resolutionDate: .fields.resolutiondate
description: '[.fields.description | .. | .text? // empty] | join("\n\n")'
relations:
project: .fields.project.key
parentIssue: .fields.parent.key
customer:
combinator: '"and"'
rules:
- property: '"$title"'
operator: '"="'
value: .fields.customfield_10309.value
subtasks: .fields.subtasks | map(.key)
jira_user_assignee: .fields.assignee.accountId
jira_user_reporter: .fields.reporter.accountId
assignee:
combinator: '"or"'
rules:
- property: '"jira_user_id"'
operator: '"="'
value: .fields.assignee.accountId // ""
- property: '"$identifier"'
operator: '"="'
value: .fields.assignee.email // ""
reporter:
combinator: '"or"'
rules:
- property: '"jira_user_id"'
operator: '"="'
value: .fields.reporter.accountId // ""
- property: '"$identifier"'
operator: '"="'
value: .fields.reporter.email // ""
Set up external tools
You need Slack and Jira API access to notify teams and update issues.
Set up Slack app
-
Create a Slack app and install it on a workspace.
-
Add the following permissions to the Slack app:
- Send messages (Required):
chat:write,chat:write.public.
- Send messages (Required):
-
Open the OAuth & Permissions page and copy the Bot User OAuth Token.
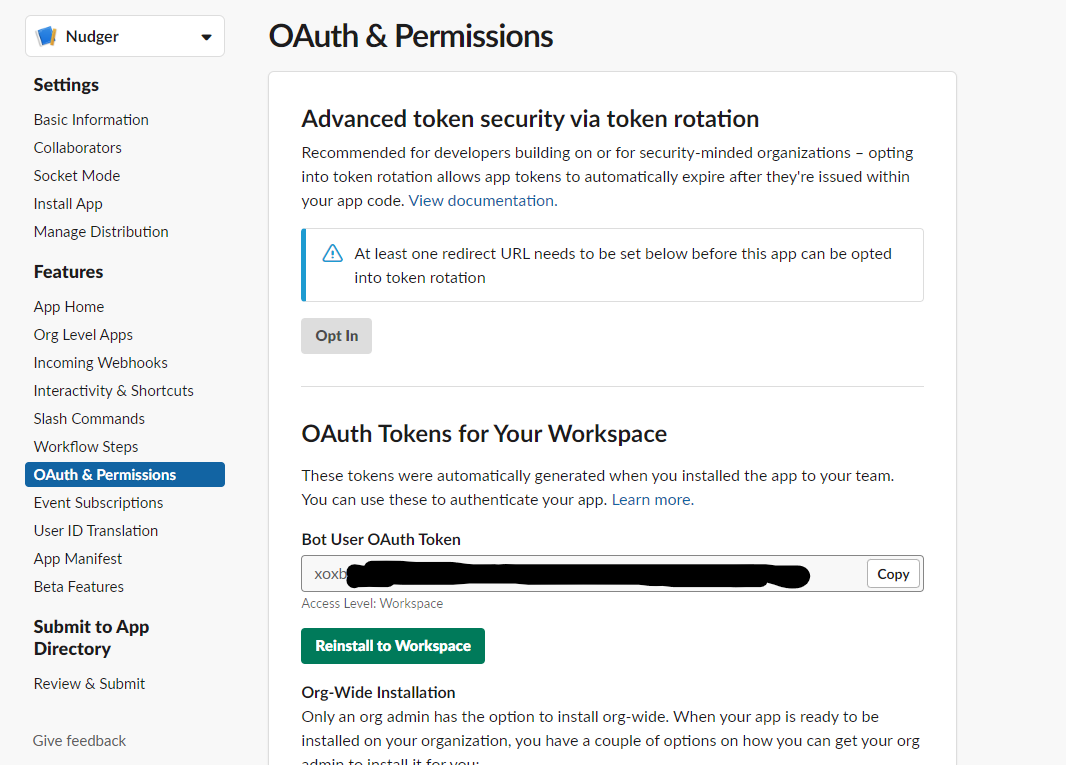
Set up Jira API access
- Log in to your Jira instance.
- Generate an API token:
- Go to Atlassian account security settings.
- Click Create API token.
- Copy the generated token for use in Port secrets.
Add Port secrets
- Click the
...menu in the top right corner of your Port application. - Click Credentials.
- Click the Secrets tab.
- Click + Secret and add the following secrets:
_JIRA_AUTH- Base64 encoded Jira credentials in the formatemail:api_token._SLACK_BOT_TOKEN- Slack bot token from the OAuth & Permissions page.
Generate a Base64 encoded Jira credential string by running:
echo -n "your-email@domain.com:your-api-token" | base64
Replace your-email@domain.com with your Jira email and your-api-token with your Jira API token.
Create self-service actions
You will create the actions that the AI agent invokes to link entities, update Jira, and notify teams.
Link issue to discovered service and team
This action stores AI discovery results on the Jira issue entity in Port.
-
Go to the self-service page of your portal.
-
Click + New Action.
-
Click
{...} Edit JSON. -
Paste the JSON configuration:
Link Jira issue to service and team (click to expand)
{
"identifier": "link_issue_to_service_team",
"title": "Link Jira Issue to Service Team",
"icon": "Jira",
"description": "AI-powered action to assign a Jira issue with auto discovered team ownership",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "DAY-2",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {
"ai_discovered_service": {
"icon": "DefaultProperty",
"type": "string",
"title": "Service Identifier",
"description": "AI discovered service"
},
"ai_discovered_team": {
"icon": "DefaultProperty",
"type": "string",
"title": "Team Identifier",
"description": "AI discovered Team"
},
"ai_assignment_reasoning": {
"type": "string",
"title": "AI Assignment Reasoning"
}
},
"required": [],
"order": [
"ai_discovered_service",
"ai_discovered_team",
"ai_assignment_reasoning"
],
"titles": {}
},
"blueprintIdentifier": "jiraIssue"
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "UPSERT_ENTITY",
"blueprintIdentifier": "jiraIssue",
"mapping": {
"identifier": "{{ .entity.identifier }}",
"properties": {
"ai_assignment_reasoning": "{{.inputs.ai_assignment_reasoning}}",
"assignment_source": "ai"
},
"relations": {
"ai_discovered_team": "{{ .inputs.ai_discovered_team }}",
"ai_discovered_service": "{{ .inputs.ai_discovered_service }}"
}
}
},
"requiredApproval": false
} -
Click Save.
Jira issue comment
This action posts an explanation back to Jira so the assignee understands why the bug was routed.
-
Go to the self-service page of your portal.
-
Click + New Action.
-
Click
{...} Edit JSON. -
Paste the JSON configuration:
Add comment to Jira issue (click to expand)
{
"identifier": "comment_on_jira_issue",
"title": "Add Comment to Jira Issue",
"icon": "Jira",
"description": "Comments on an existing Jira issue",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "DAY-2",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {
"comment": {
"title": "Comment",
"icon": "DefaultProperty",
"type": "string"
}
},
"required": [],
"order": [
"comment"
]
},
"blueprintIdentifier": "jiraIssue"
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "WEBHOOK",
"url": "https://<YOUR_JIRA_ORGANIZATION_URL>/rest/api/3/issue/{{ .entity.identifier }}/comment",
"agent": false,
"synchronized": true,
"method": "POST",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Basic {{ .secrets._JIRA_AUTH }}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"body": {
"body": {
"type": "doc",
"version": 1,
"content": [
{
"type": "paragraph",
"content": [
{
"type": "text",
"text": "{{.inputs.comment}}"
}
]
},
{
"type": "paragraph",
"content": [
{
"type": "text",
"text": "View Issue in Port",
"marks": [
{
"type": "link",
"attrs": {
"href": "https://app.getport.io/jiraIssueEntity?identifier={{.entity.identifier}}"
}
},
{
"type": "strong"
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
}
},
"requiredApproval": false
} -
Click Save.
Jira issue label
This action marks issues that were successfully assigned or need manual ownership.
-
Go to the self-service page of your portal.
-
Click + New Action.
-
Click
{...} Edit JSON. -
Paste the JSON configuration:
Update Jira issue label (click to expand)
{
"identifier": "update_jira_issue_label",
"title": "Update Jira Issue Label",
"icon": "Jira",
"description": "Adds label(s) to a Jira issue",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "DAY-2",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {
"labels": {
"items": {
"type": "string"
},
"icon": "DefaultProperty",
"title": "Labels",
"type": "array",
"description": "The labels for the Jira issue"
}
},
"required": [],
"order": [
"labels"
]
},
"blueprintIdentifier": "jiraIssue"
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "WEBHOOK",
"url": "https://<YOUR_JIRA_ORGANIZATION_URL>/rest/api/3/issue/{{ .entity.identifier }}",
"agent": false,
"synchronized": true,
"method": "PUT",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Basic {{ .secrets._JIRA_AUTH }}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"body": {
"fields": {
"labels": "{{.inputs.labels}}"
}
}
},
"requiredApproval": false
} -
Click Save.
Slack notification
This action sends a Slack message when no ownership can be resolved.
-
Go to the self-service page of your portal.
-
Click + New Action.
-
Click
{...} Edit JSON. -
Paste the JSON configuration:
Send Slack message (click to expand)
{
"identifier": "send_a_slack_message",
"title": "Send a Slack message to a dedicated channel",
"description": "Send a Slack message using the Slack app to a dedicated channel using its ID or name",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "DAY-2",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {
"text": {
"title": "Text",
"icon": "DefaultProperty",
"type": "string",
"description": "The message in a simple markdown format, Slack supported. No headings support, simple _italic_ and *bold* supported. Links supported as <text|URL>",
"format": "multi-line"
},
"channel": {
"icon": "Slack",
"title": "Channel ID or Name",
"type": "string",
"description": "The ID or name of the slack channel, e.g., C079CP2FSKV or tech-general"
}
},
"required": [
"text",
"channel"
],
"order": [
"channel",
"text"
]
}
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "WEBHOOK",
"url": "https://slack.com/api/chat.postMessage",
"agent": false,
"synchronized": true,
"method": "POST",
"headers": {
"Content-Type": "application/json; charset=utf-8",
"Authorization": "Bearer {{ .secrets._SLACK_BOT_TOKEN }}"
},
"body": {
"blocks": [
{
"type": "markdown",
"text": "{{ .inputs.text }}"
}
],
"channel": "{{ .inputs.channel }}"
}
},
"requiredApproval": false,
"icon": "Slack"
} -
Click Create.
AI agent
The AI agent uses MCP (Model Context Protocol) tools to query your catalog and run actions.
-
Go to the AI Agents page of your portal.
-
Click + AI Agent.
-
Toggle Json Mode on.
-
Paste the JSON configuration below:
Service and team auto discovery agent (click to expand)
{
"identifier": "service_and_team_auto_discovery",
"title": "Service and Team Auto Discovery",
"icon": "Details",
"team": [],
"properties": {
"description": "AI agent that automatically discovers services and team ownership for Jira issues",
"status": "active",
"prompt": "Your task is to identify the **most likely service and owning team** for a Jira issue ingested into Port.\n\nUse MCP to query the Port catalog (services, teams, repositories). Prefer **deterministic catalog data** over inference. Do not guess. If confidence is low, return `null`.\n\n### Rules\n\n* Return **at most one** service and one team\n* Do **not** invent services or teams\n* Do **not** override manual ownership\n* Assign only if confidence ≥ 70\n* If uncertain, return `null` and explain why\n\n### Discovery Order\n\n**Service discovery (in order):**\n\n1. Jira component ↔ service identifier match\n2. Name similarity (issue title/description ↔ service name)\n3. README inference (last resort)\n\nIf no service reaches confidence ≥ 70, return `service_id = null`.\n\n**Team discovery:**\n\n* If service exists:\n\n 1. `service's owning team`\n 2. `repository's owning team`\n* If no service exists: infer team from labels, issue history, or naming only if strong evidence exists\n\nIf no team reaches confidence ≥ 70, return `team_id = null`.\n\n### Confidence Signals (weighted)\n\nService: name match (+30), metadata/README (+20)\n\nTeam: owning team (+30), inferred from issue context (+20)\n\nNormalize score to 0–100.\n\n### Output (STRICT JSON ONLY)\n\n```json\n{\n \"service_id\": \"string | null\",\n \"team_id\": \"string | null\",\n \"confidence\": number,\n \"reasoning\": \"2–4 sentences explaining concrete signals used\"\n}\n```\n### Action Execution Rules\n\nYou may run the following self-service actions:\n\n* **run_link_issue_to_service_team**\n Run when confidence ≥ 70 and at least one of `service_id` or `team_id` is resolved. Always include the Jira issue entity identifier.\n* **run_update_jira_issue_label**\n Add label `ai_assigned` when assignment succeeds, or `needs_ownership` when it fails.\n* **run_comment_on_jira_issue**. Append this label to the existing issue labels \n Comment with a brief explanation of the assignment or why it could not be determined.\n* **run_send_a_slack_message**\n Run only when no service and no team can be confidently identified (confidence < 70). Strictly use #tech-general as the channel ID\n*\n\n### Mandatory Behavior\n\nYou MUST always call **run_link_issue_to_service_team** with the discovered service and/or team (even if one is `null`) to update the Jira entity in Port.\nRemember to call the **get_action** tool to understand the params and input data for all the above actions.\n\nBe conservative, explainable, and deterministic.\nIt is better to return `null` than assign incorrectly.",
"execution_mode": "Automatic",
"tools": [
"^(list|search|track|describe)_.*",
"run_link_issue_to_service_team",
"run_send_a_slack_message",
"run_comment_on_jira_issue",
"run_update_jira_issue_label"
],
"model": "gpt-5.1"
},
"relations": {}
} -
Click Create.
Set up automation
This automation triggers the AI agent when a Jira issue of type Bug is created.
-
Go to the automations page of your portal.
-
Click + Automation.
-
Click
{...} Edit JSON. -
Paste the JSON configuration below:
Discover team on Jira bug created automation (click to expand)
{
"identifier": "jira_issue_bug_discovery_automation",
"title": "Discover Team On Jira Bug Created",
"description": "Automation that triggers AI agent to auto discover team when a Jira issue is created",
"icon": "AI",
"trigger": {
"type": "automation",
"event": {
"type": "ENTITY_CREATED",
"blueprintIdentifier": "jiraIssue"
},
"condition": {
"type": "JQ",
"expressions": [
".diff.after.properties.issueType == \"Bug\""
],
"combinator": "and"
}
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "WEBHOOK",
"url": "https://api.port.io/v1/agent/service_and_team_auto_discovery/invoke",
"agent": false,
"synchronized": true,
"method": "POST",
"headers": {
"RUN_ID": "{{ .run.id }}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"body": {
"prompt": "Here is the Jira issue information:\n\nJira Issue ID: {{.event.diff.after.identifier}}\nJira Issue Title: {{.event.diff.after.title}}\n\nRelated Entities in the Catalog (for context): {{.event.diff.after.relations}}\n\nFull Jira Issue Properties:\n{{.event.diff.after.properties}}",
"labels": {
"source": "auto_discover_team_for_jira_bug",
"jira_issue_id": "{{.event.diff.after.identifier}}"
}
}
},
"publish": true,
"allowAnyoneToViewRuns": true
} -
Click Create.
Test the workflow
- Create a new Jira issue of type Bug in a project synced to Port.
- Verify the Jira issue appears in your Port catalog and the automation run starts.
- Open the
AI Invocationpage and confirm the agent executed the expected actions. - Check that the Jira issue has updated labels, assignee, and a comment with reasoning.
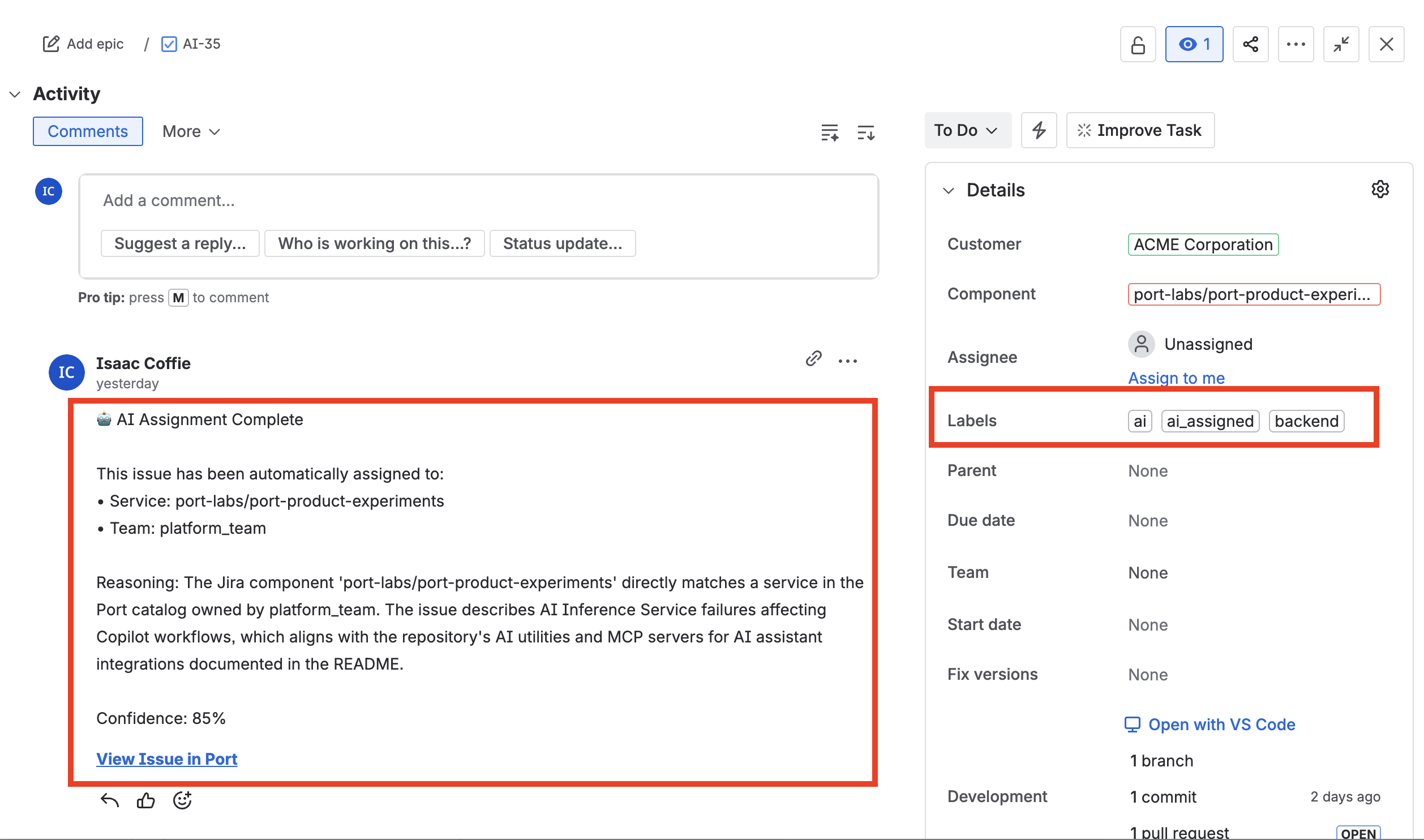
- Verify the Port entity has
ai_discovered_serviceandai_discovered_teamrelations set.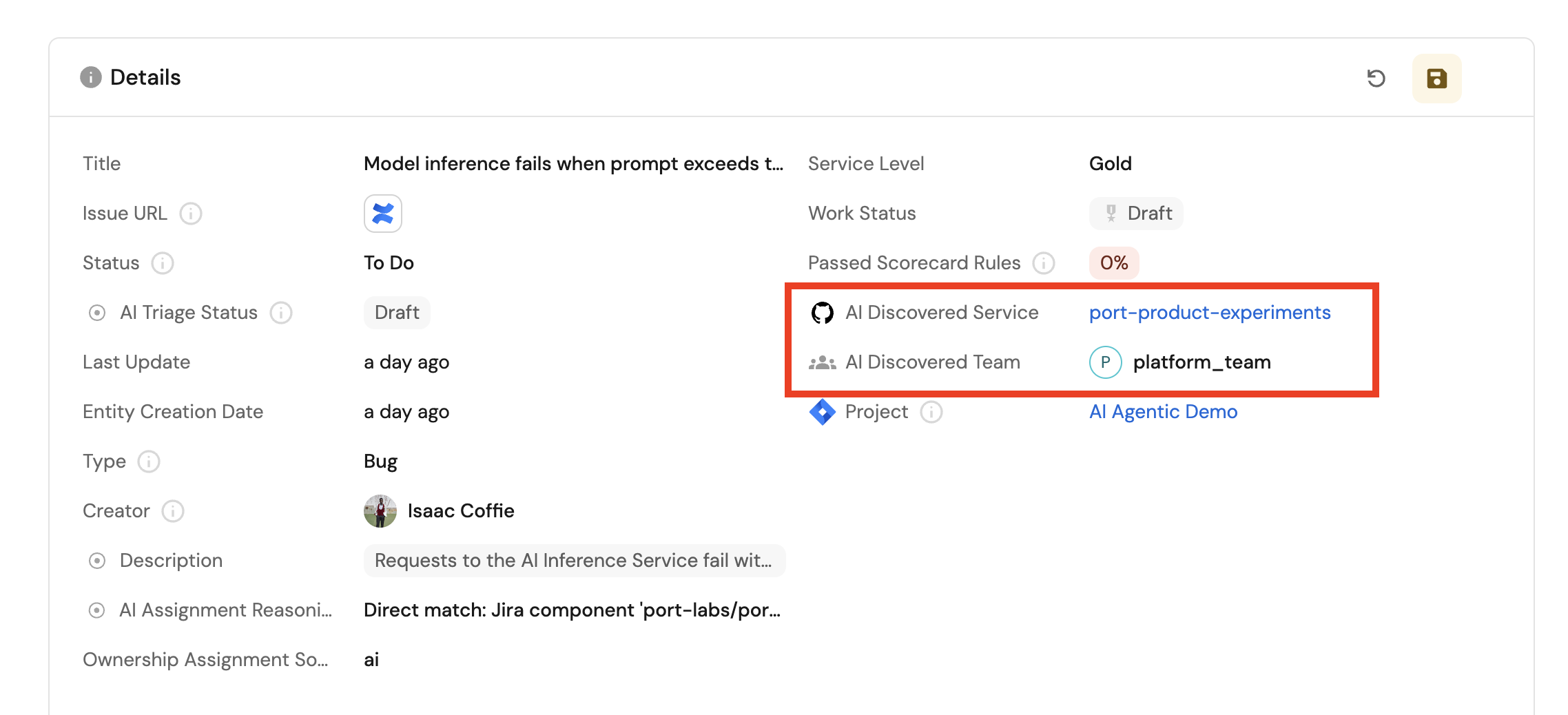
- If there is no confident ownership match, confirm a Slack message was sent to your triage channel.
